Reality Check for Retailers: Workers Need Support to Get Vaccines


As more white-collar and professional workers become eligible to receive the COVID-19 vaccine, the process for them will be easy. Sure, there may be a long wait, but thanks to a smartphone, it’s easy to check email, banter on Slack and review documents - no one will know you're away from the home office. Yet for many essential workers, including those who work in retail, sneaking away so they can get the vaccine that will make them safer isn’t quite as easy. Retail employees can’t afford to miss several hours of work – and added to the cost of taking time off to get vaccinated are expenses such as childcare and transportation costs.
Their employees’ day-to-day reality appears to have resonated with Target, which this week announced incentives that would help them score the two doses of vaccine they need. The retailer said it would pay its workers up to four hours of pay and provide up to $15 each way for rides with Lyft so they can follow through with their vaccine appointments.
For the more vulnerable communities across the U.S., tactics such as offering rides can help chip away at the continued inequity rampant across the country’s vaccine rollout.
Target’s launch of this program comes at a time when data have shown that during the nationwide vaccine rollout, people of color so far have received their vaccines at a lower rate than compared to white Americans. The retail sector is one largely staffed by women and well as racial and ethnic minorities – and the risks that come with working at these low-paying jobs are among the reasons why Black Americans have been left especially vulnerable to COVID-19.
Meanwhile, even though several of America’s largest retailers have reported a sizable increase in revenues this year compared to 2019, many of those same companies have ceased paying bonuses or any form of hazard pay to their frontline employees.
The vicious cycle continues for many retail workers: They have worked extra shifts during the pandemic, saw their pay flatline or even decrease and now face the prospect of getting vaccinated, but risk having their pay cut to go through a process that will help make their employers’ customers safer. So, credit Target for at least taking a step toward fairness.
Other retailers are dragging their feet, encouraging employees to get those two shots without any discussion of incentives. As one professor explained, the lack of any incentives makes no sense as herd immunity will not only benefit only employees, but their companies’ customers. A few hours of paid time off is a small yet wise investment.
“Why the heck would you not?” said Denise Rousseau, professor of organizational behavior and public policy at Carnegie Mellon University's Heinz College, to USA Today. “You want to encourage people to take the vaccine.”
Other retailers, including Aldi, Lidl and Trader Joe’s have announced similar programs that include paid time off, a cash bonus – or both.
Some executives have couched these cash bonuses as a way showing “support” for their employees, though today’s cost of living merits more support than a $200 check if retail workers will be fairly compensated for going through hoops necessary to prevent them from getting sick with COVID-19. The bottom line is that these vaccine programs are protecting their businesses and the communities in which they operate. At this point, supporting vaccination efforts isn’t about corporate responsibility; it’s table stakes.
Image credit: Jpesch95/Wiki Commons
Money Talks: Racism on Trial in $2.7 Billion Lawsuit Over Voter Fraud
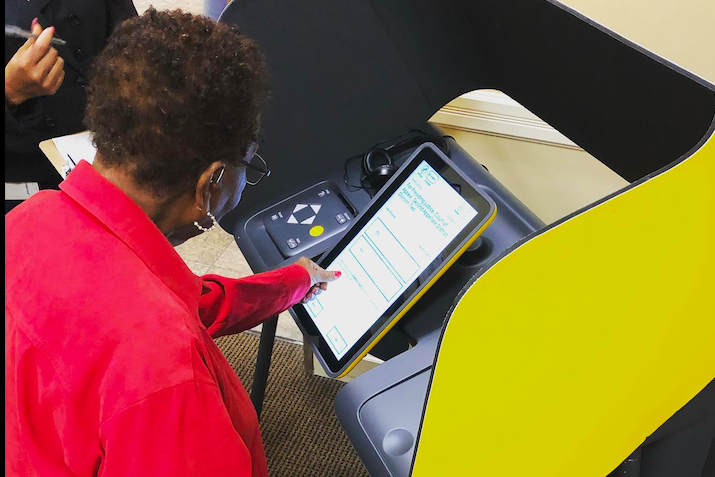


Photo: A Los Angeles County voter casts her ballot using a Smartmatic voting machine. The company has since pushed back against allegations of voter fraud in a $2.7 billion defamation lawsuit.
Former U.S. President Donald Trump is frequently described as a racist, a reputation that long predates his election to office in 2016. Nevertheless, Fox News has been among the media outlets choosing to risk brand reputation by amplifying and validating Trump’s claims of voter fraud, which election observers and civil rights advocates have characterized as race-based. Now Fox, along with several of its hosts and guests, is facing a lawsuit that puts a $2.7 billion price tag on racism.
Race, voter fraud accusations and suppression
Voter suppression has all too often taken a murderous turn throughout the history of the U.S. Seen through that lens, Trump’s well-documented series of lies about voter fraud appears to be part and parcel of a long history of white-on-black voter suppression violence, with a deadly ripple effect on white allies of Black voting rights advocates.
In the weeks following Election Day 2020, a number of media organizations noted that Trump and his allies focused their claims of voter fraud on cities and counties with large populations of Black and non-white voters, leading civil rights advocates and other election observers to state that race-based voter suppression was integral to the claim of widespread voter fraud.
The failed insurrection of January 6 validated that view of Trump’s voter fraud strategy. Considering the history of violence surrounding race-based voter suppression in the U.S., it is not surprising that the takeover of the Capitol Building was no peaceful occupation. It was a violent invasion with intent to terrorize if not kill.
Smartmatic and brand reputation
When the Black Lives Matter movement gathered renewed force last summer, it helped to focus corporate leaders on structural racism and voter suppression, motivating some to double down on get-out-the-vote efforts.
However, Trump and his allies were already poisoning the well in the weeks leading up to Election Day 2020.
TriplePundit was among those warning that the get-out-the-vote drives only marked the beginning of a longer, more arduous fight against voter suppression after Election Day.
That warning was borne out by the behavior of Fox News, which continued to make ample space in its schedule for lies about voter fraud in the weeks following Election Day.
One of its chief targets was the voting technology firm Smartmatic. A global firm with a solid reputation, Smartmatic has yet to establish a broad footprint in the U.S. In fact, its activity in the 2020 election was limited to a single jurisdiction, Los Angeles County in California.
Nevertheless, according to the company’s tally Fox “made over 100 false statements and implications about Smartmatic.”
“The overall theme of the disinformation campaign was that Smartmatic fixed, rigged, and stole the 2020 U.S. election,” the company has stated.
Smartmatic has filed a $2.7 billion defamation lawsuit in the Supreme Court of New York State that details each of the allegations and describes how the impact on the company’s international reputation has suffered financially. The impact continues to ripple out, even though U.S. election professionals from both political parties insist that there was no evidence of widespread fraud in the 2020 election.
The real work on fighting voter suppression is only just beginning
Smartmatic CEO Antonio Mugica has argued that the impact of the Trump voter fraud campaign goes beyond its own brand reputation and bottom-line concerns.
“One of the biggest challenges in the Information Age is disinformation,” he explained. “Fox is responsible for this disinformation campaign, which has damaged democracy worldwide and irreparably harmed Smartmatic and other stakeholders who contribute to modern elections.”
As Mugica warned, Smartmatic has become collateral damage in a broader, existential threat to democracy, and the damage continues to unfold after the January 6 insurrection.
Having failed to accomplish through violence what democracy denied, the Republican Party is turning to new legislation that disproportionately has an impact on the vote of Black and non-white citizens, among other voter groups supportive of Democratic candidates.
On January 26 the Brennan Center for Justice published a list of new state bills related to elections and voting, noting that “after historic turnout and increased mail voting in 2020, state lawmakers across the country are pulling in opposite directions by introducing restrictive and expansive voting legislation.”
“New legislation reflects a surge of bills to limit voter access, with a particular focus on mail voting and voter ID,” the Brennan Center elaborated in a February 8 update.
Business leaders who are serious about standing up for Black lives, people of color, and American democracy itself have their work cut out for them in the weeks and years to come.
Cutting off advertising dollars is one means of forcing media organizations like Fox to behave more ethically, an area in which the grassroots boycott campaigns Sleeping Giants and Grab Your Wallet have proven effective.
The Smartmatic lawsuit ups the ante by seeking to demonstrate that Fox’s role in the voter fraud lie has been malicious as well as unethical and immoral.
That already appears to have had some impact. Fox abruptly fired host Lou Dobbs, who is named in the Smartmatic lawsuit, within 24 hours after the lawsuit was filed.
However, CNN business reporter Alexis Benveniste notes that the firing may be just one piece of a pattern in which Fox fires one or two personalities, while enabling damage to fester under the surface in other areas.
That strategy has worked in the past. For example, boycott campaigns are credited with the cancellation of host Bill O’Reilly’s slot in 2017 over sexual harassment, and yet Fox was not dissuaded from allying itself with an efforts to overturn the results of the 2020 election.
Another red flag is the involvement of wealthy individuals, such as the Mercer family, Trump mega-donors who are can continue to support media and social media organizations whether or not any substantial revenue comes in. The Mercer family network, for example, has included Breitbart News and Parler in addition to the data firm Cambridge Analytica.
Responsible corporate leaders should be aware that the anti-democratic movement has been a strong, running thread throughout American history, requiring constant vigilance to support the ideal of free and fair elections.
Corporations that have halted PAC donations to the 147 Republican members of Congress who objected to the 2020 Election have made a good start, but there is much work to be done.
In addition to withdrawing campaign dollars from state legislators who support voter suppression bills, corporate leaders could make a real difference by supporting candidates and legislators who seek to expand voter access instead of stifling them by false accusations of voter fraud.
After all, money talks.
Image credit: L.A. County Registrar-Recorder/Facebook
Walgreens and Uber: We’ll Drive You to Get Your Vaccines
Vaccinating 330 million Americans – many of whom view vaccines and the government with mistrust – has already proven to be a tall order. The nationwide effort is going to require endless hustle, creativity and a plan so the most vulnerable and isolated get their shots to prevent the spread of COVID-19. But cross-industry partnerships are in the works. In December, for example, Lyft and Anthem announced a plan to offer rides to citizens who are eligible and ready to get their vaccines.
Now Uber says it’ll join that effort through a partnership with Walgreens.
The companies announced yesterday they will work together to take on the challenges inherent with vaccine distribution by adopting a three-pronged approach: education, access and technology.
The plan calls for a pilot program to run in cities such as Atlanta, Chicago, El Paso and Houston. Together, the companies say they will provide up to 10 million free or discounted rides to Walgreens locations and vaccine clinics. Goals include making the process as easy as possible: For example, Walgreens says it will be easy to schedule a ride for a vaccination appointment with one click on a device. Uber says it will help meet the demand by also deploying drivers who deliver for Uber Eats and Uber Freight.
Of course, not everyone has smartphone or is comfortable using technology, which in part has contributed to an ongoing lack of vaccine equity. Further, plenty of citizens are hesitant to schedule their vaccines in the first place. To that end, the companies say they are working with the National Urban League to roll out an educational campaign to tackle those concerns.
Such outreach is crucial, as early reports have suggested Black Americans across U.S. states and cities are currently being vaccinated at a rate significantly lower than their share of the local population – and in many states, demographic data isn’t being reported at all. The discrepancy has been persistent coast-to-coast, from Los Angeles to New York.
So, the challenge only isn’t about fear; many of the people who should be at the front of the vaccination line still haven’t been contacted and hence are in the dark. California, which has lagged on vaccination compared to much of the nation, has realized that looking at zip codes to ensure people of color get vaccinated is a start – but the state’s government also needs to plan so it can prevent those who have easy access to vehicles simply don’t drive to places like the Oakland Coliseum and cut in line to get their shots at the expense of communities of color.
Transportation is part of that equation, hence ride-hailing companies like Uber have the opportunity to do their part – and also repair their brand reputations, too. The healthcare sector would also be wise to look at partnerships akin to the Uber-Walgreens alliance; deflecting blame and pointing fingers at certain communities months down the road simply isn’t fair.
Public health workers have put both government and the private sector on notice. “Vaccine hesitancy is a real concern, but I worry that focus on vaccine hesitancy is a way to deflect responsibility for equitable distribution on the front end,” said Anne Sosin of the Dartmouth Center for Global Health Equity in a recent interview with Politico.
Image credit: Fernando Zhiminaicela/Pixabay
Ew, David! Schitt’s Creek Offers Companies a Cautionary Tale on Diversity


Image: Filming Schitt’s Creek in Goodwood, Ontario, in 2018.
Much needs to change within government, business, and the media if all of us are to reach our potential and feel included in society. One television show in particular, however, has shown what it means to walk the walk on inclusion and acceptance, rather than simply talking about it. I am, of course, sharing lessons about Schitt’s Creek, the Canadian sleeper series that slowly became a cult favorite, then a huge hit and cleaned up during the most recent Emmy awards, just after it aired its final season.
Why there’s no Pride Month in Schitt’s Creek
The show’s characters are imperfect, and yes, the main characters are white: Though, in fairness, a father and son duo conceptualized the show and the actor playing the show’s patriarch, Eugene Levy, has known the actress who played his on-screen wife (Moira, played by Catherine O’Hara) for over 40 years.
Those relationships set the tone for the show’s six-season run. For LGBTQ fans of the show, the strength — and joy — of Schitt’s Creek is that David Rose, played by Daniel Levy, isn’t just another gay man (technically he’s pansexual) who yet again is everyone’s foil on the show because of his sexuality.
There’s no tortured coming out process — which is more painful in real life than onscreen anyway — and there are no lectures about homophobia as David is simply a part of his family. Unfortunately for him, he’s also part of the motel and that godforsaken town in the middle of nowhere, so his foibles are more about the wannabe “it” boy as a fish out of water, not based on who he sleeps with.
Ditto David’s relationship with Patrick, one that focused on each of their quirks and the tensions that emerge from running a business together — not the fact they are a gay couple. If anything, their relationship is one of the most wholesome ever shown on television.
Recent promotion of the show also gives insight on living and working authentically. When Schitt’s Creek and its network launched the final season last year, one of its billboard ads showed the couple kissing — far and away more meaningful than the stock images of Pride celebrations that companies dust off every June during their summer public relations campaigns.
The town runneth over with folks who speak truth to power
If anything, one lesson for the office or virtual Zoom meeting is the show’s insight on how to deal with entitled people: David and the rest of the Rose clan often bump through their new life with a dismissive attitude, only to find the people who Moira dismisses as “townies” won’t have it.
And many of those townies are people of color who aren’t afraid to speak truth to power — with the caveat that in Schitt’s Creek, power is defined by the former CEO of the second-largest video chain in North America during the VHS era.
One of the show’s best characters is Ronnie (played by Karen Robinson), who confidently dishes out deadpan, no-bullshit delivery with a breathtaking honesty many of us wish we could see in the office. Ronnie’s interactions with the Rose family don’t come out of resentment or an unfair power dynamic — she simply doesn’t care that Moira once hosted the non-televised portions of the People’s Choice awards. Capability and competence, not status or titles, are what matters in Schitt’s Creek — even the town’s doofus mayor, whose job is defined by birthright, isn’t immune from challenges to his authority.
Some critics have pointed out what they perceive to be the lack of diversity in Schitt’s Creek, but again, we’re discussing a family-run show (three members of the Levy family are in the cast) that had almost no budget.
The bottom line is that the show’s characters aren’t afraid to speak their mind, which executives should consider when it comes to race and gender. Allowing employees to speak the truth, and not assume it’s only their truth, is the first step in forming a truly inclusive work culture. Plunking a press release full of boilerplate language about Black History Month, Pride or gender equity is simply another way a straight white cis male says, “Sure, we’ll have a conversation about diversity, inclusion and equity but on the C-suite’s terms.”
Be honest about your DEI challenges
Finally, addressing diversity in an honest way is the final lesson Schitt’s Creek offers us. As the show continued to generate more buzz and awards — even after it was long known it had filmed its final season — criticism also mounted. The actor playing the town’s jack-of-all-trades-master-of-none, Rizwan Manji, was called out for playing into stereotypes about Indian males. Manji pointed out that the choice for how Ray was portrayed was his alone. He added, however, that many of the characters on the show weren’t “fleshed out,” lacked any backstory and instead were there for comic relief. Scanning through the show’s 60 episodes, however, shows that the Rose family more often than not was the butt of ongoing jokes, including that of Ray’s.
Dan Levy’s response to Manji’s criticism offers a short and concise master class on how to address those diversity challenges when someone’s called out. He wasn’t defensive about other’s points of view and added, “That said, I welcome any perspectives that encourage conversations about diversity, especially in entertainment.”
In the end, when companies are challenged about their work culture and the lack of diversity in their ranks, the way to win trust is to allow those conversations in the first place. Papering over the concern of your employees with a public statement saying you “stand with” a community doesn’t say much. Writing a check and sending it to a community is a step, but if you didn’t include your employees in making that decision, the end result is kicking the inclusion can down the road.
If Ronnie, Ray, Carol and Marnie can speak truth to the patriarchy, executives at America’s most powerful — and still very white — companies can do the same.
Image credit: Shutterstock
Ride-Hailing Services Could Accelerate Acceptance of EVs


Electric vehicles (EVs) market gained a staunch supporter with the election of President Joe Biden, but motivating millions of drivers to go gas-free is still a daunting task. According to some experts, the U.S. needs to add 50 million EVs by 2030 to help meet its Paris climate commitment. Because the window for action is so tight, resources to stimulate the transition must be carefully planned and targeted. Ride-hailing businesses, also known as transportation network companies, may provide one such opportunity.
The importance of the transportation company network
The use of ride-hailing is growing, but transportation network companies (TNCs) still account for a relatively small share of miles driven in the U.S. In terms of prioritizing resources, that would seem to indicate that TNC electrification is not a particularly effective area in which to focus attention and resources.
However, the think tank RMI (previously known as the Rocky Mountain Institute) suggests that TNCs do have the potential to make a significant impact on EV adoption. The organization recently took a deep dive into the topic, based on TNC data provided by GM – and calls for an electrification campaign focused on the likes of Uber and Lyft.
The report outlines three reasons why TNCs should be an area of focus. First, individual TNC drivers could be more persuadable from a simple bottom-line perspective. The up-front cost of buying an electric vehicle is still higher than a comparable gas-powered car, but lifetime maintenance and fuel costs are lower. TNC drivers spend more time behind the wheel, so they are in a better position to appreciate the lifetime cost-of-ownership benefits of electric vehicles.
According to RMI’s analysis, a full time TNC driver in the U.S. travels about three times more miles than the average driver, meaning that electrifying one TNC car would have the same carbon impact as electrifying multiple privately used vehicles.
Another benefit involves the potential to increase access to public high-speed EV charging stations. As more TNC drivers go electric, that creates more demand for charging stations. TNC drivers could serve as “anchor tenants” that make it worthwhile for EV charging firms and public planners to build more charging stations in more diverse areas of a city or town. The benefits would ripple out to other drivers including delivery van fleets and other commercial vehicles.
Finally, TNC drivers can serve as EV ambassadors to large numbers of people. Compared to other drivers, TNC drivers encounter many more people in the course of their day. With each ride, they provide an opportunity for the public to become familiar with the EV experience.
“By converting conventional gasoline ride-hailing vehicles to electric, we simultaneously eliminate dangerous tailpipe emissions and leverage the rapidly decarbonizing power sector to reduce overall vehicle carbon emissions,” RMI observes. “In addition to the direct benefits, paving the path for ride-hailing electrification will do the same for electrification in other transportation segments.”
EVs: opportunities and obstacles
The opportunity to electrify TNC drivers is technologically do-able in terms of the vehicle itself, but financial obstacles remain.
RMI suggests that more TNC drivers would make the switch if there were more pathways to lowering the up-front cost of EVs. In addition to subsidies, the options would include an increased emphasis on leasing or renting, and marketing used EVs.
That problem may become moot in several years. GM and other auto makers anticipate that the up-front cost of EVs will attain parity with gas-powered cars by the middle of the decade, largely due to improvements in battery technology.
Partnering for rapid progress
That leaves the issue of charging infrastructure, a key consideration in urban areas where individual drivers don’t have the opportunity to install home charging stations.
RMI advises ramping up coordination between EV stakeholders, and that is an area in which GM may come into play.
GM has already begun to invest in the public fast-charging infrastructure, in anticipation of widespread EV adoption within the next several years and 100 percent electric mobility over the long run. Last summer GM teamed with the firm EVgo to introduce 2,700 new charging stations around the country, all to be powered with renewable energy.
The company is also focusing on the e-commerce and delivery van market through its new BrightDrop venture. BrightDrop launched last month following a successful pilot run with FedEx, which has committed to buying 500 of the firm’s new EV600 electric vans. Last week the national fleet management company Merchants Fleet upped the ante with a 12,600-van commitment.
The Merchants Fleet connection brings GM into contact with a fast-growing, innovative firm that influences fleet managers at a national scale, raising the potential for a significant impact on the demand for public fast-charging stations.
Gig workers and climate action
The new RMI report was supported in part by the green philanthropy ClimateWorks Foundation, which is positioned to focus stakeholders and investors on electrifying TNC drivers.
Still, hanging over the area of TNC electrification is the broader issue of the gig economy, its impact on worker rights, and its ripple effect on other job opportunities.
The COVID-19 pandemic has exacerbated the festering gig worker issue, and gig worker rights took a giant step backwards last year with the passage of Proposition 22 in California.
If TNC drivers are to play an important role in EV adoption, it is possible that auto makers like GM could help build a path forward that eases the risk of exploitation from the gig worker field.
GM may be in a position to help motivate change through its relationship with Merchants Fleet, which has taken up a leadership position on workforce education and training.
The automaker could also apply its long experience with labor unions to help improve conditions for TNC drivers, but that remains to be seen.
Image credit: Bram Van Oost/Unsplash
A Short Story of Fuel Efficiency Standards and America's Auto Industry


For years now, America’s auto industry has faced an uncertain regulatory future regarding fuel efficiency standards, which had been resolved in 2012 when the Obama administration imposed tough but achievable requirements through 2025. In doing so, desired regulatory certainty was achieved with the backing of all major automakers under a national program.
Background on the fuel efficiency standards debate
U.S. automakers always want to build vehicles to meet a single national fuel efficiency standard as otherwise they must manufacture cars to multiple specifications. For example, California’s requirements are based on the state’s longstanding EPA waiver, allowing the state to set stricter standards at its discretion. Aligning the federal government’s and California’s regulatory paths keeps things simple.
Although the Obama administration set a single national standard creating the uniformity and certainty the industry wanted, with the advent of the Trump administration and its anti-regulatory stance, the auto industry bifurcated. Half of the industry saw an opportunity to agitate for looser efficiency standards that they would prefer to live with.
Ford, Honda, BMW, Volkswagen and Volvo, however, opted to stick with more ambitious targets and struck a deal with California to track more closely with Obama-era rules in accordance with the state’s EPA waiver. Conversely, General Motors, Fiat-Chrysler and Toyota, among others, decided to push for a relaxation of efficiency standards, believing that the stricter Obama-era rules would force them to build vehicles the public didn’t want. The Trump administration, happy to lend a sympathetic ear, embraced the opportunity to jump into action.
Turning back the clock – and MPG requirements
Trump’s EPA did two things. Firstly, the agency relaxed fuel efficiency standards, altering the mandated 54.5 mpg requirement to 40 mpg for model year 2026 for cars and light-duty trucks. Secondly, the EPA sought structural change designed to defang California’s influence.
The Trump administration attempted this by filing a lawsuit seeking to end the EPA waiver California had enjoyed, backed by those automakers wanting looser regulation. Since California is the largest vehicle market in the nation, removing the state’s ability to self-regulate would have been the Trump administration’s ace up its sleeve to set a new, nationwide and less stringent set of fuel efficiency standards.
But after the November election, with the Trump administration defeated it was all unfinished business, resulting in the last four years for the car industry looking like this: Uncertainty once again over fuel efficiency requirements and an auto industry itself divided over a desired regulatory framework.
An election, and a shift
The story continues, though. A combination of a Biden win, technological advancements and an auto industry seeing emerging global regulatory realities means there is new potential for the industry to realign under a single more ambitious national regulatory standard once again.
And in this post-election moment, General Motors might prove to be at the fulcrum of the turnaround, albeit accidentally.
The company has been somewhat of an enigma during the recent past. Though aligning with the Trump administration’s efforts to relax fuel efficiency standards, GM concurrently forged ahead with plans for its own “all-electric future” along with a pledge to sell only emissions-free vehicles by 2035; an incongruent stance between what it was building and what it was lobbying for.
But Biden’s win in the general election likely nudged GM to reverse course on its regulatory ambitions. By mid-November, GM announced it was abandoning its participation in the legal fight over California’s waiver, and as the New York Times reported at the time, it seems GM’s CEO, Mary Barra’s decision to withdraw from the lawsuit was based on the imminently changing political landscape.
And then last week, with GM - one of the biggest players - already out of the lawsuit, the challenge to California’s waiver fell apart completely. The remaining automakers backing the end to the state’s waiver announced that they would no longer seek to block California from setting its own fuel efficiency standards. These developments since November could start to bring the auto industry back into alignment with one another, organized around renewed targets.
As various sources reported, the Biden administration is already working on crafting new fuel-efficiency standards with the EPA. The result could align national regulations with California's requirement of 51 mpg by 2026 - albeit with a national standard likely pushed back a year or two.
Automakers must confront an all-electric reality
Rulemaking will, of course, take some time. But it also opens up the possibility for ambitious zero-emissions goals in years to come. California’s governor, Gavin Newsom, already signed an executive order for emissions-free vehicle requirements by 2035, which environmental groups will likely push for nationally, too.
These targets also align with the emerging global context in which automakers find themselves. The United Kingdom has already said it will go all-electric by 2035, while the European Union is targeting 30 million electric vehicles (EVs) to drive on its roads by 2030. Since auto manufacturing is a global business, the momentum towards increased efficiency standards transcends America’s borders and will surely signpost what products companies will spend their research and development dollars on.
Finally, technologically, things have moved on since the push first began to relax standards at the advent of the Trump administration. Battery prices continue to fall. Bloomberg reports that in 2020 battery costs were 13 percent lower than the year before, falling to around $137 per kWh. Furthermore, the holy grail of $100 per kWh should be achieved by 2023, at which point EVs will reach price parity with internal combustion engine cars.
Putting this all together, the Biden administration now has the opportunity to unify the industry by sealing long term regulatory certainty the automakers desire, based upon higher standards of efficiency and more ambitious goals, in line with an industry which faces new global realities.
Image credit: Jack Gisel/Unsplash
Nominations for 2021 Responsible CEO of the Year Awards, Lifetime Achievement Award Now Open


Has the head of your company reached that elusive sustainability mountaintop? If you believe so, then take note: The 3BL Media team recently announced the launch of nominations for the 13th annual Responsible CEO of the Year Awards and 10th annual Lifetime Achievement Award.
Considering what we have all experienced over the past year, responsible corporate leadership has taken on a whole new meaning, especially in an era during which government has either refused or has been unable to lead during times of crises.
Following a time in which we witnessed a once-in-a-century pandemic affect every corner of the globe, the loud calls for racial and economic equality, threats to democratic institutions, and more climate-related disasters, the reality now is that stakeholders expect companies to take unprecedented action by showing leadership on these challenges.
But before any organization can act as a true force for good, there must be authentic buy-in at the top.
Details on the nomination process can be found here.
Be sure to have your team complete the nomination form and send all materials to ResponsibleCEO@3blmedia.com by March 31, 2021. To be clear: There are no costs to nominate your organization’s CEO.
A unique set of awards focusing on the business community, Responsible CEOs are playing an active role in ensuring their organizations deliver on environmental, social, governance (ESG) commitments.
Similarly, the Lifetime Achievement Award recognizes an individual whose career-long commitment to progress has driven significant achievements in the corporate responsibility and sustainability space.
All awardees are nominated by fellow members of the ESG community and are then selected by an independent panel of past recipients and recognized leaders. Finalists will be notified in June and asked to produce a video no longer than three minutes by July 31.
Be sure to check out the full list of past award recipients here. Past recipients of the Responsible CEO of the Year Awards include the leaders of Aflac, CVS Health, Danone North America, the Girl Scouts of America, LG Electronics, Porter Novelli, PwC, VF Corp. and World Central Kitchen.
Image credit: Alfred Aloushy/Unsplash
How to Make Financial Well-Being a Priority in Uncertain Times


Between the economic downturn and COVID-19, consumers are under immense financial pressure at a time when it’s more important than ever to think about saving money and planning for a stronger, post-pandemic recovery. Even amid such great uncertainty, there are still ways to save, get control of debt and credit, and boost financial well-being.
Financial well-being may seem out of reach for many people grappling with heightened unemployment as they grapple with the ongoing pandemic and its impacts. The slowdown in the U.S. economy as a result of COVID-19 has affected every sector of society:
The U.S. workforce is down nearly 10 million jobs since February and the economy is operating at roughly 80 percent of its pre-pandemic activity.
While many individuals and businesses may feel unsettled during this unprecedented economic blow, that is all the more reason to not neglect one’s financial health, says finance expert and Capital One partner Farnoosh Torabi.
“Many people are financially challenged right now. They may have lost a job, face mounting debt or are living paycheck to paycheck. But as difficult as this time is for so many people, it is also an opportunity,” Torabi told TriplePundit. “I think we’re all recognizing in this pandemic what we really value. Our lifestyles pre-pandemic may not actually have been aligned with our needs versus our wants.”
We spoke with Torabi and other financial experts to find out how people at any income level can take control of their personal finances and begin to improve their financial health when it matters most.
To start saving, get back to the basics
Cultivating a savings mindset requires going back to the basics, Torabi explained.
“What have we learned about ourselves since the pandemic began, and how is that reflected in our budget?” Torabi said. “Are there things that you can cut out immediately like a website subscription or a gym membership you don’t use? Maybe it won’t be forever but just to shore up some much-needed cash.”
She also said that it’s important to tie savings to a financial goal that is personally motivating.
“Whatever that might be — being able to move out of your parent’s house, pay down credit card bills or have the cushion to enable you to quit your job — what are the long-term goals you want to reach?”
Having different types of bank accounts, from checking to savings to retirement accounts for long-term investing, can help hit those goals. For example, to prepare for unexpected expenses, Torabi suggests aiming to save up to 6 months’ worth of our basic living expenses — or as much as you can afford — into an emergency savings account that is separate from investment accounts designated for retirement.
“Our money serves different purposes,” Torabi said. “There's money that we need today. There's money that we may need in three to five years and then there's money that we don't want to touch for the next 30 years. It doesn't make sense to have it all in one place because we want that money to grow differently.”
She also says it’s key for people to lean into their support systems.
“There are a lot of resources out there that can support you,” Torabi said. “It might also be a friend you trust and can confide in who keeps you accountable. Just as with any big goal, there's power in the collective and momentum in working with others. Studies have shown that when we announce our savings goals to others, we are more likely to not only save but to save more than what we had initially set out to do.”
Use your resources
One available resource is SaverLife, a nonprofit that helps people build financial security and a Capital One partner. With 470,000 members, SaverLife aims to give working people the methods and motivation to take control of their financial future. Those interested can sign up at saverlife.org.
The median income for members is $25,000 and more than 80% of members are female or are parents.
“This is really aimed at the essential worker that has kept his or her country running during the last several months,” says Tania Brown, a certified financial planner with SaverLife.
Membership has shot up by 270 percent since the pandemic began and SaverLife has distributed a total of $3 million in emergency cash grants hardest during the pandemic. “This is the moment we’ve been saving for,” said Shana Beal, director of communications for SaverLife. “This is the time when suddenly everyone is focused on savings because so many people lost their jobs so quickly.”
SaverLife members were more prepared than most to weather the economic crosswinds. According to the organization, pre-pandemic, within six months of joining SaverLife, members more than tripled their savings rate and 52 percent deposited $500 or more into their savings account. SaverLife members save 14.2 percent of their income, compared to the 2019 national average of 7.7 percent. And its members are diverse: 40 percent white, 33 percent Black, 12 percent Latino, and 8 percent with multiple backgrounds.
Shift your mindset
In addition to providing budget tools, SaverLife gamifies saving by awarding points to users as they build their financial health, which can be redeemed for digital scratch cards with a chance to win cash prizes. The approach centers on “making savings easy and fun,” Brown said. “So even if you’re not ready or don’t know how much you can save or if you’ve never done it before, we want to encourage people to start as small as possible, a few dollars a week. Once it becomes a habit, no matter how small the amount put aside, the savings will keep growing.”
With 40 percent of American adults unable to cover a $400 emergency with cash, savings or a credit-card charge they could quickly pay off — even before the pandemic — “savings is the last line of defense to make sure there is food on the table, the bills are paid, that there is a roof over your head,” Brown told us. “When you start to look at it as insurance, it then becomes a priority. Life is going to happen — a drop in income, an illness, some unexpected life expense — and you need that savings in place as an insurance.”
Among the strategies that SaverLife advises for its members is automatic savings through payroll deductions. Another tip is to purchase a gift card for the purpose of dining out to limit that expense. “Once the card is gone, it’s gone,” Brown said. “That preserves the amount you intended to save.” Additionally, when an unexpected amount of money comes in — whether it’s a gift, a bonus or a refund — make it a practice to put at least half of that money into savings, Brown suggested. “I always emphasize to people it is the consistency over the amount,” she said. “Savings will always go up if you’re consistent.”
Overall, SaverLife sees savings as an important component of a more equitable U.S. economy, something Brown can relate to personally. “I grew up poor. I grew up on public assistance,” she told us. “I could go back to where I grew up and throw a stick and hit a payday lending place, a check-cashing place. When you think about all the components that go into what would be considered the American dream — owning a home, being able to retire — every single component of a more equitable world in terms of wealth starts with savings. When we have equity in terms of knowledge and what savings behavior looks like, people can start to develop those habits and build a better future for themselves and their families.”
Work to make financial well-being a priority
“People are dealing with so many stressful factors right now, and many people are feeling anxiety around [financial] issues,” said Kim Allman, senior director of community impact and investment for Capital One. “And while not everyone is in the same financial situation, people should make financial well-being a priority, if they can.”
Of course, this is easier said than done, but as Allman observes, even small savings allocations add up over time — and small mindset or lifestyle changes can make a big difference. “Taking action to set goals, identify and address roadblocks, and make plans can help empower individuals and help them prepare for the future,” Allman told us. "This can help to meet immediate needs as well as needs that may arise in the future.”
Capital One partners with organizations like SaverLife as part of its mission to “change banking for good” by removing barriers to opportunity and creating pathways to financial success. Building on this track record, the company recently announced the Capital One Impact Initiative, an initial $200 million, five-year commitment to support growth in underserved communities and advance socioeconomic mobility by closing gaps in equity and opportunity. That includes initiatives aimed at racial equity, affordable housing, small business support, workforce development and financial well-being.
“Financial empowerment isn’t just about information and awareness. We want to give people the tools they need to feel confident in their relationship with money, remove barriers and create channels to action,” Allman said. "We believe that finances should work for everyone, no matter where they are on their financial journey.”
This article series is sponsored by Capital One and produced by the TriplePundit editorial team.
Image credit: iStock Photo via Capitol One
In Colombia, Comuna 13 Shows How to Get Inclusive Tourism Done Right
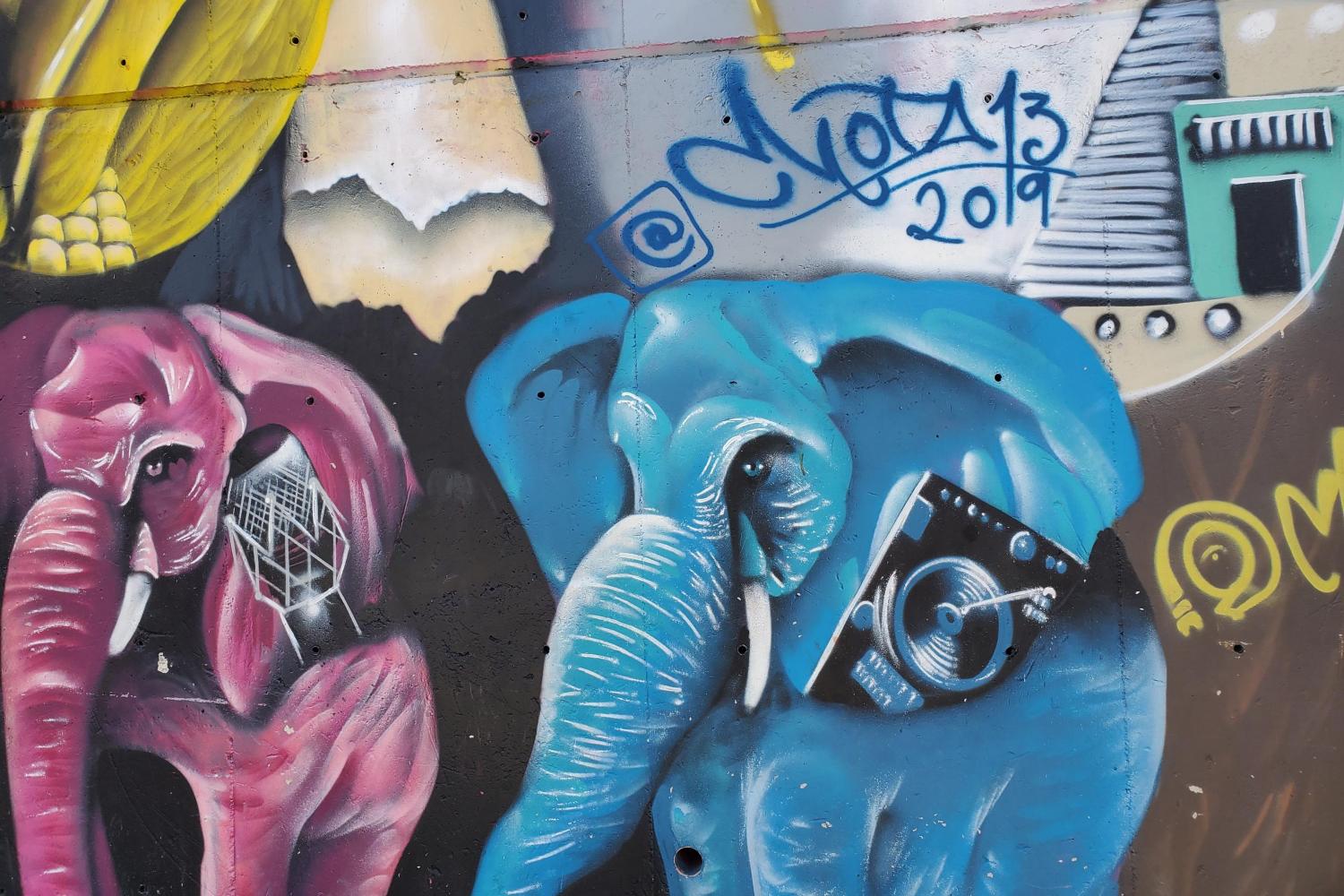
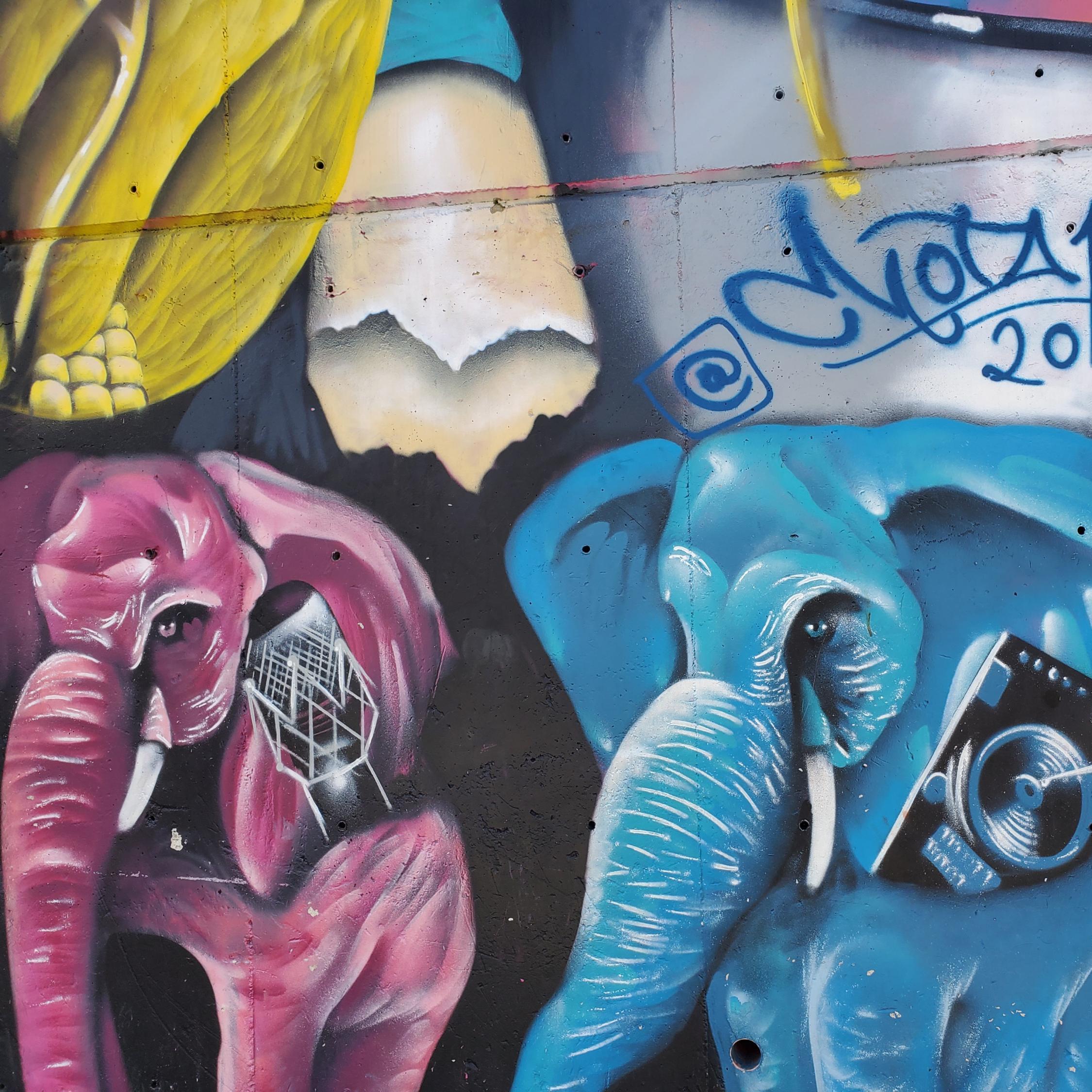


Photo: A mural in Medellín’s Comuna 13. Elephants are a frequent image seen in Comuna 13, as they represent strength and a reminder to honor the memory of its people’s past.
There’s no shortage of reasons to visit Medellín, Colombia’s second-largest city, once the world re-emerges from the global pandemic. Among the highlights, the city is a laboratory showcasing what can work in 21st-century urbanism; offers access to spectacular mountains and historic towns; boasts a vibrant and welcoming culture to visitors of all backgrounds; is home to a thriving cycling scene; and showcases spectacular public art.
Comuna 13, a district on the city’s outskirts, is also a must-see for how it offers a view of the country’s troubled past and perspective on just how far the city has come in recent years.

Understanding Colombia’s past
To understand why Comuna 13 should land on anyone’s itinerary during a visit to Medellín, an understanding of Colombia’s history is crucial.
Here’s the Reader’s Digest version: After the assassination of a leading presidential contender in 1948, political violence soon spread across much of rural Colombia. Farmers and their families often found themselves settling in the mountains surrounding cities such as Bogotá and Medellín. The new, rapidly settled neighborhoods lacked any infrastructure, but that didn’t stop Medellín from tripling in population between the early 1950s and early 1970s. Those same hillside communities became socially isolated, lacked any viable transportation that could take their residents to decent paying jobs in the city center, and — as too often depicted in popular culture — they were consumed by violence during the 1980s and 1990s.
One of the defining moments in Comuna 13’s history, and that of Colombia, was Operation Orion in October 2002. The military incursion removed leftist rebels who dominated the district, but also terrorized over 100,000 residents who found themselves exposed to the crossfire, which injured hundreds and left dozens missing. In turn, that operation helped spark the rise of right-wing paramilitary groups who critics say at times still harass locals to this day. Reminders of that tragedy are apparent in the murals found throughout Comuna 13 today.

Fast forward to 2021, and while Medellín and all of Colombia still grapple with vast income inequality, poverty has overall decreased in the city and surrounding region of Antioquia. Medellín’s crime rate, according to many travel writers, suggests that it’s safer than many U.S. cities, and the city of 2.6 million now has its share of shiny hotels, swank restaurants, big-box stores and shopping malls.
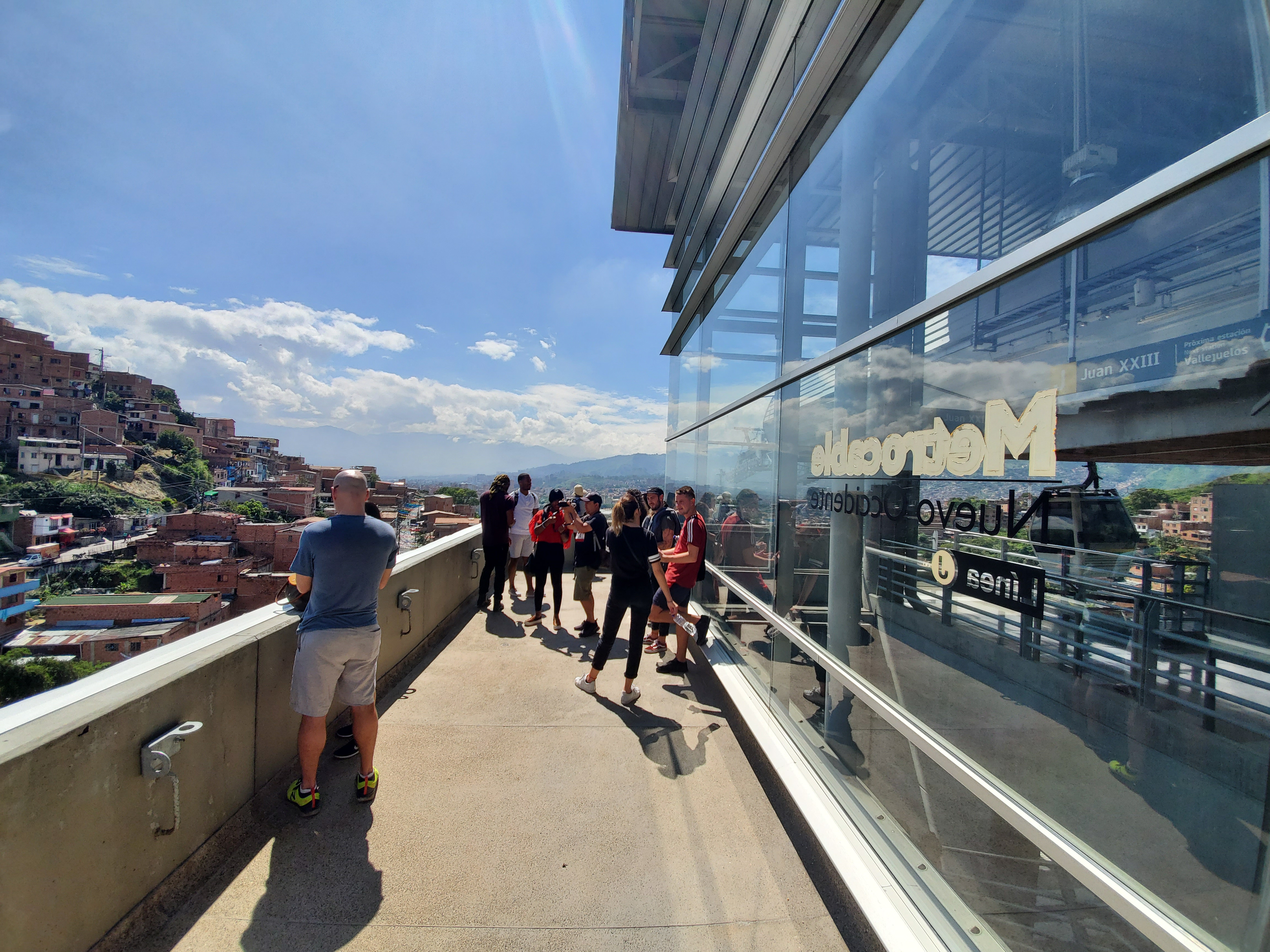
In recent years, one success Medellín’s political leadership achieved is that hillside communities have become further integrated with the city. The local metro system connects to MetroCable, an aerial cable car system that ferries residents to and from such neighborhoods as Comuna 13. A 1,300-foot escalator, launched a decade ago, also helps connect residents to the rest of the city, avoiding traffic gridlock or a difficult trek up and down the neighborhood’s streets. Neighborhoods once separated by the terrain and therefore dominated by rival gang factions are now linked by pedestrian bridges.
Visiting Comuna 13 today
The neighborhoods within Comuna 13 still have their struggles with poverty and other problems endemic in poorer communities. Yet Comuna 13 has largely reemerged as a vibrant community rich with a spirit of entrepreneurship, vivid street art, tempting street food and a history well worth learning.
Experiencing Comuna 13 is far from the voyeuristic “poverty porn” that has long revealed an uglier side of tourism, from the Harlem bus tours of the 1980s to the group trips still offered so visitors can witness some of the world’s poorest neighborhoods today.

The first task is finding a legit tour, but thanks to websites and apps full of crowdsourced content like TripAdvisor or MeetUp, locating a stellar local tour guide shouldn’t take long. The trick is to find someone who will take you to Comuna 13 via local public transportation. The tour I booked with the Comuna 13 Graffiti Tour group, for example, arranged to have our group of 12 meet at one of Medellín’s central metro stations. Not only did that approach allow everyone in the group to experience the city’s rail system, but the ride also gave our tour guide time to explain the context of the afternoon excursion. From our Metro stop we switched to a local city bus — yes, it was clear to locals this was a dozen gringos stepping off the bus upon their arrival at Comuna 13, but traveling on local transport felt far less intrusive.
During any tour of Comuna 13, common sense reigns. Face it, locals will know you're visiting, but be aware of how you conduct yourself and how and where you wield you camera. These tours have been ongoing for several years now, so the chances are high that you’ll notice residents simply carrying on and minding their own business. For the less adventurous, there are plenty of cafes and venues with English-language menus and signs for restrooms. Yet despite the measures to make visitors from abroad feel comfortable, a tour of Comuna 13 is still a very local experience — the vast majority of tour guides not only live within Medellín, but were, or still are, residents of this district.
Local tourism, on locals’ terms
While most tour guides will insist you don’t wander too far off and use common courtesy when snapping photos, our guide gave us about a half hour at the end of the tour to do our own thing – within reason. That gave our group time to enjoy the views, buy local art, a freshly silkscreened t-shirt, or nosh on a paleta, a frozen treat best described as a gourmet frozen fruity popsicle (and far better). A bar that offered spectacular views of the mountains surrounding Medellín also served up the best fresco de aguacate (avocado smoothie). Depending on where your guide takes you, there will be plenty of time to sample arepas (cornmeal cakes), empanadas (savory turnovers) and plantains prepared in countless ways.
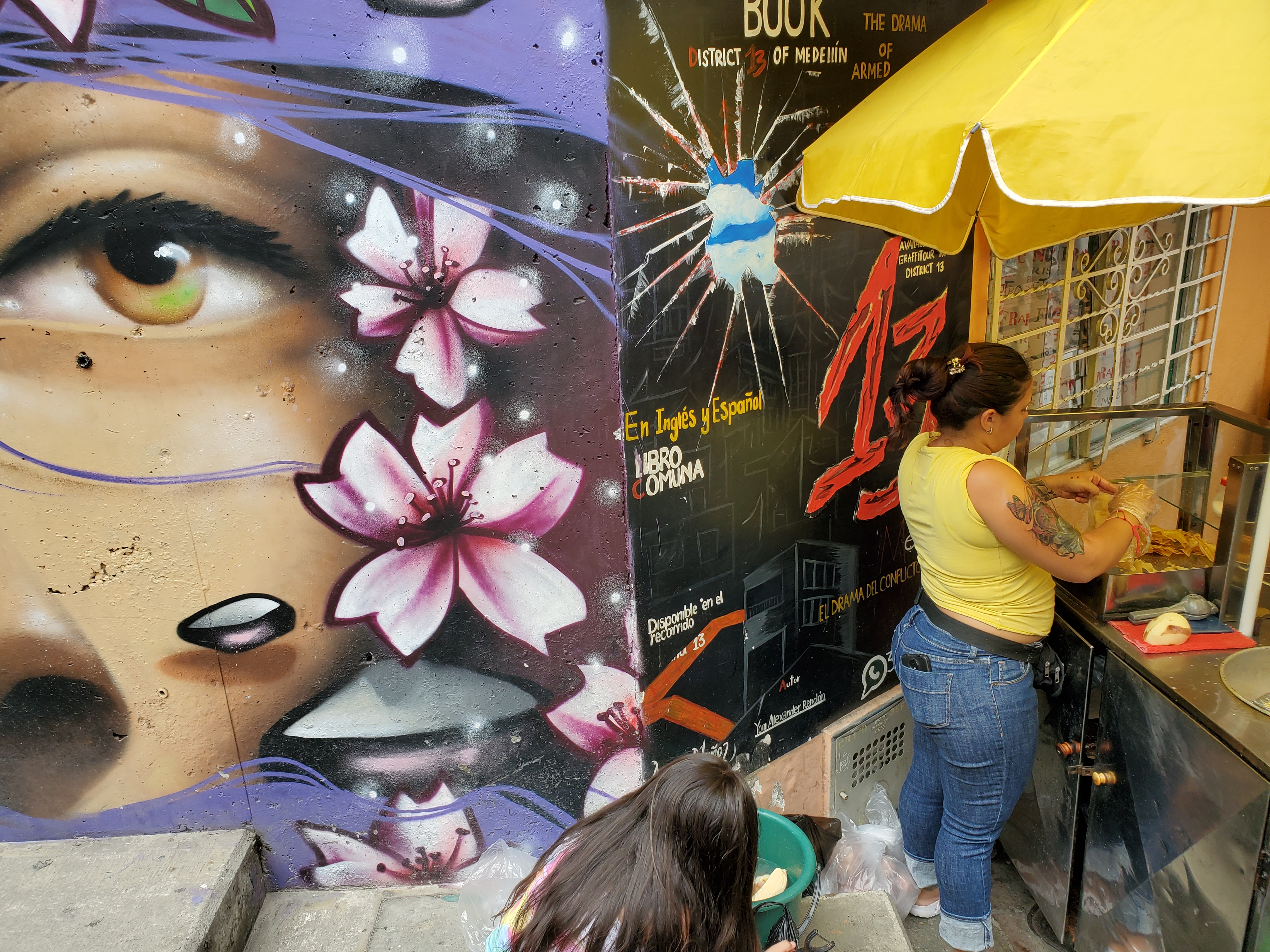

The ongoing transformation of Comuna 13 makes it a compelling case study in social enterprise. In addition to the street vendors, this community has also become a haven for artists, among them Chota13, the art of whom can be found on the sides of buildings and retaining walls. Art is also available for sale in various media, from wall hangings to sneakers. As more cities across the globe look to Medellín as a case study from which they could learn how to revitalize their neighborhoods, graffiti festivals and competitions also became regular events before the pandemic. Local businesses also benefit from social programs the city of Medellín has funded, including childcare and classes for skills development.
The problems many Colombians still confront daily haven’t all gone away. Nevertheless Medellín, and Comuna 13, together offer plenty of lessons in civic engagement, showing that a blend of the right investment, strong local leadership and earning the trust and buy-in of residents can improve a neighborhood’s quality of life and avoid exploiting its people. Touring Comuna 13 also shines new light on how tourism can be driving not by the urge to make quick buck, but by allowing people to tell their own story, on their own terms.
Image credits: Leon Kaye

For Black Women Entrepreneurs, Access to Resources is as Crucial as Cash


By just about every measure, Black women are the most entrepreneurial demographic group in the U.S. Yet companies led by women of color CEOs score far less than 1 percent of all venture capital funding. The numbers don’t add up, and in a very unfair way – leaving many black women entrepreneurs scrambling to find other sources of financing.
The encouraging news is that more companies realize they can play a role in reversing inequities rampant across the U.S. economy. They also understand that action requires more than writing a check and issuing a public proclamation that they stand with women of color.
One such company is American Express, which last fall announced a $1 billion slate of programs seeking to boost racial, gender and ethnic equity for all of its stakeholders – from employees to customers to the communities in which it conducts business.
Among those programs is Amex’s “100 for 100” program, which in November selected 100 black women entrepreneurs to receive grants $25,000 and 100 days of access to resources. The latter part of the program kicked off last month and is teaching and mentoring on such topics as managing cash flow, maintaining business relationships and navigating through this current economic environment.
Amex is partnering with organizations including IFundWomen (IFW), a social enterprise that works with women entrepreneurs to provide opportunities for capital, business coaching and a network of mentors and other professionals willing to share their expertise.
One success story coming out of this program is LaToya Stirrup, who founded Kazmaleje (pronounced “cosmology”), a manufacturer of hair accessories. Stirrup and her two sisters launched the company in 2019, only to be thrown a huge curve ball last year as the pandemic wreaked havoc on new companies. Amex’s 100 for 100 program counted Stirrup among this group of Black women entrepreneurs, and the new funding and mentorship has allowed her company to course-correct and continue to grow.
Furthermore, Kazmaleje has been able to entrench itself in the hair accessory market for a couple reasons. As Stirrup recently explained to Yahoo Finance, first, the company was able to show it was an essential business. As many women could no longer go to the local salon due to lockdowns, those with curls needed something to help them deal with the fact their hair was growing out. In addition, Stirrup and her company has since partnered with Repurpose Global, a platform that works with companies like Kazmaleje to go plastic-neutral and reduce waste within their supply chains. Judging by the company’s Instagram feed, the company is thriving.
Companies like Kazmaleje had the vision and knew their target market. What they needed was a lift in the form of capital and resources that could get them over the proverbial hump – access long granted to plenty of companies over the years, but often denied Black women entrepreneurs because they didn’t quite have the right connections and networks.
Image credit: Brandy Kennedy/Unsplash