Climate Change is Worsening Water Scarcity: How Business Can Help


About 4 billion people live in water-stressed areas and face severe water scarcity during at least one month each year. Over a billion more — including 1 in 4 children — will live in areas of extremely high water stress by 2040. Climate change is already disrupting weather patterns, leading to extreme weather events, causing unpredictable water availability, worsening water scarcity, and contaminating freshwater supplies.
As major water users, manufacturers have an influential presence in communities worldwide. More specifically, multinational businesses can use their scale to play a significant role to protect the watersheds where they do business and forge partnerships with governments, nonprofits, and other community stakeholders who are best poised to understand the intricacies of local water problems.
Water scarcity poses risk to companies — and climate change is making matters worse
Already, companies must consider the realities of available resources on the ground and factor in other stakeholders that might be in competition for those resources. Climate change only exacerbates this tension. In fact, in its 2021 Global Risk Report, the World Economic Forum listed failure to act on climate change as a top risk impact for the global economy, second only to infectious diseases.
Water scarcity, specifically, poses a major risk. The World Bank predicts a growth rate decline of 6 percent of global GDP by 2050 as competition for water intensifies across all sectors. While these figures are stark, opportunities exist to create innovative solutions to these challenges. Companies are better poised to drive faster change, and due to the risks they face, it is in their interest to do so.

A personal connection gives way to a global solution
For Vetri Dhagumudi, global water program leader for Kimberly-Clark, these issues are personal as well as professional. He grew up in Chennai, India, a city of 11 million people that nearly ran out of water in 2019, despite historically being one of the wettest cities in the world.
“As a child, growing up with no water was normal,” he told TriplePundit. “Every day, someone’s duty was to pump water from a hand pump. We had no water as part of a daily routine, and then when it rained, you walked to school [in] waist-high water.”
Dhagumudi trained as an engineer focused on wastewater management, but it wasn’t until he started working in the Arizona desert that he realized how much his life had always been connected to water. He often thought about Chennai, where the community seemed to continuously struggle to develop a solution that worked for them.
“There were many solutions in the market,” Dhagumudi recalled, “but it was hard to see what works best. How do you find a solution? I decided to focus on the whole water spectrum.” That led to Kimberly-Clark’s co-creation of WaterLOUPE a tool for water-stressed areas similar to Vetri’s own life experiences growing up in Chennai.
Mapping risk at the watershed level eases business-community partnerships
Launched on World Water Day in 2018, WaterLOUPE was developed through a partnership between Kimberly-Clark and Dutch research organization Deltares. The tool visualizes current and future scarcity risks for entire watersheds on a user-friendly dashboard, with the aim of supporting multi-stakeholder decision-making and collaborative action. “Water is emotional,” Dhagumudi said. “The whole idea of WaterLOUPE was to create a scientific discussion, not an emotional one, so the water users could make the best-informed decisions.”
In order to enable the most comprehensive view of a particular watershed, WaterLOUPE tracks data relating to social, economic and climate factors that affect freshwater availability. “As soon as someone says ‘water risk,’ you think water reduction, but that’s not the only solution,” Dhagumudi continued. “We need to understand water supply demand, the socio-economic factors, population, economic development, risk of water conflicts, biodiversity, and urbanization.”
Watershed partners in Cape Town, South Africa; São Paulo, Brazil; and Cali, Colombia, already use the tool — which combines national and local data with scenario modeling to create risk models and associated solutions.
Notably, though, WaterLOUPE is not meant to be a plug-and-play solution. An intensive stakeholder process happens first. Getting the data is one thing. Having people buy into it is another. “We spend eight or nine months before the engagement workshop getting everything lined up,” Dhagumudi said. “You must consider how every location has its unique challenges. What works in Cape Town doesn’t work in São Paulo. We have to have people who understand the culture, the bureaucracy, and pull the science up through the emotion and the politics.”
Felipe Godoi, senior environmental engineer at Kimberly-Clark’s Mogi das Cruzes facility in São Paulo, added: “It’s extremely important to design the tool based on local specifics, so industry, government, and community can together understand the present and future scenarios with the purpose of minimizing the impacts of water scarcity through strategic decision making.”
The entire countries of Israel and Bahrain now have WaterLOUPE studies in progress, with the aim of mapping watersheds at the national level.
Kimberly-Clark and Deltares will launch WaterLOUPE 2.0 on World Water Day, March 22. This new dashboard can assess possible measures that help mitigate future water scarcity risks, as identified by local stakeholders. The methodology and tool will enable local stakeholders to choose one or multiple solution strategies using scenario modeling to visualize if the water gap and related risks can be minimized, as well as quantify water shortage, risk reduction and economic consequences. Using this tool, local stakeholders in the water basin will be able to visualize the risk and interventions that close the water scarcity gap.
Addressing water scarcity challenges on a global scale
Unfortunately, no region is immune from water stress. Many wet areas will go dry, and dry areas will strain under exacerbating conditions. Multinational companies with manufacturing or other operations in multiple countries will see these issues compound with climate change, and it behooves them to proactively work with local leaders to find pragmatic and fair solutions.
No one company or stakeholder can solve a region’s water problems — the realities are too complex, too emotional, and involve too many interests. A company can set a goal for zero water use, but it will have little impact on the local watershed if other major users in the area do not also change their practices. Put simply: Working together is the only option.
While the climate changes across the globe, impacts are felt locally. Water in particular is hyper-local, and its importance means it’s also hyper-political. As something we all touch every day, it is also emotional. Using the best scientific data is essential to find the right solutions, but at the heart of this problem are the people who are affected by increasingly scarce water supplies.
Bringing the story full circle, Kimberly-Clark and its partners are taking the tool to Chennai because of the dire need for innovative water solutions. But for Dhagumudi, it means he can be involved in making things better for his hometown. “It’s satisfying to go back home.”
This article series is sponsored by Kimberly-Clark and produced by the TriplePundit editorial team.
Image credits: kazuend and Mark Rohan via Unsplash
Leading Companies Start Taking Action on Shipping Emissions


The task of curbing shipping emissions is like turning around the proverbial ocean liner. With massive amounts of fuel involved, the transition to a more sustainable oceangoing transportation scenario will be slow and cumbersome. Nevertheless, the job has to be tackled, and a group of leading shippers is working towards a collaborative solution.
U.N. asks for a ‘propulsion revolution’ to curb global shipping emissions
The global shipping industry has been identified as a leading contributor to global warming. In 2019 the United Nations warned that the current state of affairs would lead to “an environmental disaster,” and advised that the industry requires a “propulsion revolution” to decarbonize.
The industry has already undergone at least one major technology revolution in modern history, when cargo vessels transitioned from wind-powered sails to fossil-powered engines. The next revolution will need to be even more wide-ranging and intensive.
To support the U.N. goal, 80 stakeholders in the global shipping industry formed the Getting to Zero Coalition in 2019, partnering with the Global Maritime Forum and Friends of Ocean Action, along with the backing of the World Economic Forum and the World Resources Institute.
GZC has a mission to establish an industrywide roadmap for cutting shipping emissions by at least 50 percent by 2050. As of this writing there are 140 members and a roadmap has taken shape.
New technology is not enough
Last November, GZC committed to five action steps outlined in a report prepared by the Energy Transitions Commission.
In terms of accelerating climate action, the good news is that technology to reduce shipping emissions is already in hand. However, the report makes it clear that ship builders will not commit to new fuels and technologies without the full backing of all stakeholders.
New technologies exist, but they are untested at scale on deep-ocean vessels. The supply chain has yet to materialize at scale as well. The report envisions a “first wave” of commercial-scale, deep sea pilot vessels supported by cost-reducing and de-risking strategies. That will require the backing of government policy makers and other stakeholders, including those required to create new value chains.
The report outlines five collaborative steps for overcoming these obstacles: fast-track new technology; target locations with renewable energy access; re-use or retrofit existing infrastructure; form co-investing ventures for vessels, fueling equipment and other critical assets; and form consortiums to develop the demand-side market.
New technology is not good enough
Another point to consider is whether or not the latest generation of new fuels and technologies can apply to large deep-sea vessels.
For example, the mainstreaming of electric vehicles and the growth of the green hydrogen market suggest at least two pathways to zero-emission oceangoing vessels.
However, under today’s technology the logistics are formidable. Last week Guardian reporter Fiona Harvey outlined some of the obstacles:
"There are severe logistical difficulties with decarbonizing shipping: an electric ship, for instance, would require the equivalent of 10,000 Tesla batteries a day to cross the Atlantic. Hydrogen is another proposed fuel, but… on current estimates it would take 60% of the world’s renewable energy generation to produce enough hydrogen to power shipping.”
Harvey’s reporting suggests that a fuel and technology solution is not up to the job of cutting shipping emissions quickly.
She notes that the International Chamber of Shipping is backing a $2 levy on every metric ton of shipping fuel, with the aim of raising $500 million annually for R&D on zero emission vessels. The proposal has been submitted to the U.N. International Maritime Organization. Greece, Japan, Switzerland, Singapore, Malta, Nigeria, Liberia, Georgia and Palau, which represent 40 percent of commercial shipping, have already signed on in support.
However, Harvey reports that the Environmental Defense Fund (EDF) and other climate action groups have charged that the levy is inadequate and would distract from more effective carbon pricing strategies.
Going off-road on the decarbonization roadmap
Despite the obstacles, the shipping industry will decarbonize - eventually. Maersk and other industry leaders have already invested significant sums in zero-carbon research and development, though progress has been slow. Maersk’s showpiece carbon neutral project, for example, is a smaller vessel designed for regional hops rather than deep-sea travel.
The real problem is how to achieve a more rapid, significant reduction in shipping emissions over the short term.
One strategy under discussion is slow steaming, which simply refers to reducing the speed of a vessel. According to some estimates, reducing ship speed by 10 percent can reduce emissions by 27 percent. That scenario is not as rosy as it may seem, considering that more ships would be needed to fill the same transport capacity.
Overall, the switch to slow steaming could reduce carbon emissions by almost 20 percent, but shippers may balk at the need to hire more crew in addition to investing in more ships.
A more holistic solution would be to regionalize manufacturing, in order to reduce the need for overseas shipping overall. The emergence of locally sourced materials, 3-D printing and other new manufacturing technologies could help. However, there is little prospect of the global shipping industry getting behind such a proposal.
Consumers could also make a difference, by making lifestyle changes that support the plastic-free movement and other strategies for reducing waste and consumption. Again, it would be difficult to rally shipping stakeholders to support movements that reduce the number of ships at sea.
Meanwhile, here in the U.S. President Biden has yet to announce specific plans for decarbonizing maritime industries.
However, a strategy appears to be coalescing with the appointments of Energy Secretary Jennifer Granholm, Transportation Secretary Pete Buttigieg, and EPA chief Michael Regan. Along with coordinating on policy-based solutions, the three agencies will likely ramp up their collaboration on technology R&D.
In addition, the Department of Defense could play a significant role in pushing new technology R&D. The Navy has been an early adopter of biofuels and other carbon-reducing strategies, for example.
The change of power in Congress also bears watching. Earlier this year the National Law Review took stock of the pent-up momentum for change building in the Biden administration, including the introduction of the Ocean-Based Climate Solutions Act by House Democrats last October.
Among other carbon-reducing measures, the bill would encourage voluntary speed reduction in the Exclusive Economic Zone.
The bill would have likely died in a Republican-controlled Senate, but the 2020 election cycle has provided Democrats with a slim majority in the Senate.
With all this in mind, it’s little wonder that the Getting to Zero Coalition continues to grow its membership, the latest addition being China’s GAC Group. As the National Law Review notes, “stakeholders who fear the uncertainty of new environmental regulatory standards are advised to engage early in the process.”
Image credit: Jimmy Nguyen/Unsplash
State-Sanctioned Voter Suppression, Brought to You by America’s Leading Corporate Citizens


Having failed to enable the takeover of the U.S. federal government by force, Republican legislators are now relying on new state-based voter suppression laws to rein in Black voters, among others. This new push for voter suppression laws has exposed last year’s corporate-supported voter drives as little more than a game of whack-a-mole. The real power rests with the elected officials who make election law, and now some unwanted attention is now turning on the corporate donors who helped put them in office.
State-based voter suppression bills rise from the ashes of failed insurrection
The failed insurrection of January 6 is coming into sharp focus as an organized attempt by white supremacists to overthrow the U.S. government. They were incited and legitimized by former President Trump’s aggressive amplification of voter fraud lies. They were also enabled - wittingly or not - by the 147 Republican members of Congress who supported the Trump voter fraud campaign by raising spurious objections to the Electoral College results in several key states.
The mob eventually cleared out from the U.S. Capitol Building on January 6, but the white supremacist movement continues to lean on the voter fraud canard to justify more than 250 new pieces of state legislation aimed at making it harder for Black voters, and other likely groups of voters who at a minimum lean Democrat, to cast a ballot.
Where does corporate America stand?
In the days following January 6, several leading U.S. corporations recognized the reputational risk of helping insurrection enablers into office. They announced that they were withholding donations to PACs associated with all 147 Republican members of Congress who objected to the Electoral College certification. Others pledged to review all of their PAC donations.
However, the exceptions proved the rule. By February, the movement to inflict financial punishment on insurrection enablers lost steam. Even as the number of state-based voter suppression bills climbed into the hundreds, corporate America made no organized attempt to defend its own position on voter rights.
In an apparent attempt to provide cover for corporate donors, last week the U.S. Chamber of Commerce issued a memo arguing that the 147 Republican insurrection enablers did not deserve to lose corporate support simply because they cast a vote.
“Casting a vote is different than organizing the rally of January 6th or continuing to push debunked conspiracy theories,” the Chamber wrote, neglecting to specify that the votes of January 6 were cast in support of the voter fraud conspiracy theory that was supposedly debunked.
Brand reputation at risk
The state-based voter suppression effort has finally begun to catch media attention. Particular attention is being paid to Georgia as the most egregious example. Not coincidentally, last year a massive get-out-the-vote drive sent Black voters to the polls in numbers high enough to deliver their state to Joe Biden as well as Kamala Harris, the nation’s first Black vice president; in a January runoff election, they sent Rev. Raphael Warnock, Georgia’s first Black U.S. Senator, into office.
With Georgia Governor Brian Kemp on the verge of signing new voter suppression bills into law, it seems that the brand reputation chickens have come home to roost.
Editor's note: Be sure to subscribe to our Brands Taking Stands newsletter, which comes out every Wednesday.
Independent journalist Judd Legum has been tracking the flow of corporate dollars, and last week he drew attention to a new campaign that links corporate donors to voter suppression efforts. The campaign was launched by the Georgia NAACP, New Georgia Project, and Black Voters Matter, targeting leading household brands including Coca-Cola, Delta, and Home Depot along with Aflac and Southern Company.
The campaign also name-checks the Georgia Chamber of Commerce, the Metro Atlanta Chamber of Commerce and the Georgia Black Chamber of Commerce.
By yesterday afternoon, major Georgia-based companies including Coca-Cola, Delta and Home Depot said they were either aligned with the Georgia Chamber's pushback against this legislation or put out a statement in support of voting rights.
In particular, Legum cites the New Georgia Project, which issued a statement underscoring the hypocrisy of corporate support for Black History Month even as new voter suppression bills worked their way to the Governor’s desk.
“Simply put, being a good ally means showing up for marginalized communities when they are under attack,” NGP wrote. “Despite organizing Black History Month campaigns and using Black Lives Matter slogans, many corporations in Georgia support lawmakers working to disenfranchise Black voters, while others remain mum on the issue entirely.”
A corporate game of get-out-the-vote whack-a-mole
Legum has also been turned attention to corporate links in another voter suppression hotspot, Arizona. Culling through “thousands of Arizona campaign finance records filed over the last three years,” he identified hundreds of thousands in corporate donations to Republican elected officials sponsoring 22 voter suppression bills.
Last week, Legum reported that two corporate donors, Union Pacific and Prudential Financial, went on the record in opposition to the most egregious of the Arizona bills.
However, he also excoriated other corporations for remaining silent about voter suppression bills, including Farmers Insurance Group, Blue Cross Blue Shield Association, Wells Fargo and General Motors.
In particular, Legum singled out Cox Communications:
“Cox Communications (Cox), for example, touts its commitment to "voting rights and justice for all" on its corporate website. In the run-up to the 2020 election, Cox partnered with Rock The Vote and Vote Safe 2020 to encourage people to exercise their voting rights. ‘[P]atriotism and civic duty is in our DNA," the company said in a tweet, ‘It’s our belief to do the right thing, always.’”
Legum also called out Pinnacle West for the hypocrisy of supporting suppressive legislators with one hand, while the other hand the company is associated with a leading Arizona business group that is pushing back against voter suppression.
The group, Greater Phoenix Leadership, published an op-ed on March 3 that drew a bright line from the Republican voter fraud canard to the wave of voter suppression legislation:
“These proposals are a concerted effort from those in Arizona - and across the nation- who wish to sow additional doubts about our elections in the minds of voters, and feed into the paranoia that has plagued our political discourse over the past several months. Disturbingly, each of these proposals have one thing in common – making it more difficult for Arizonans to vote.”
Mainstream media takes notice
Corporate links to state-based voter suppression efforts are now in the crosshairs of mainstream media, aided by the high profile of Georgia-based voting rights activist Stacey Abrams.
On March 15, Forbes turned up the heat by publishing an editorial by Senior Contributor Michael Posner, who made case for the U.S. Chamber of Commerce to establish voter suppression as a disqualifying criterion for corporate support.
“Leading business associations like the Chamber should not reward candidates who are limiting the right to vote. Nothing less than the integrity and vitality of our democracy is at stake,” Posner wrote.
It remains to be seen if the public attention finally compels corporate supporters of voting rights to organize a more vigorous defense of their efforts. As of this writing, the U.S. Chamber of Commerce is still making weak excuses for itself and providing cover for its members.
Image credit: Manny Becerra/Unsplash
Impact Investing Is Sitting on a $30 Trillion Nest Egg


If you had $1 trillion in your bank account, you could buy the Miami Marlins one thousand times. Now, imagine you have the power to purchase the Miami Marlins… thirty-thousand times over. $30 trillion is the amount of wealth that is likely to pass down from baby boomers to Gen Xers and millennials in the coming decade. In addition, nearly 87 percent of millennial investors believe investing should go beyond pure profits, according to one 2018 survey. However, not all of us have a plump enough purse to host grandiose competitions, such as Elon Musk’s XPrize carbon removal competition.
What opportunities exist for ordinary investors who want to put their money to good use? Luke Wilcox, founder of the fintech start-up Ethos, recently sat down with TriplePundit to explore the nascent world of impact investing.
ESG or impact investing?
Both ESG (environmental, social and governance) and impact investing are under same broad financial umbrella, but have key differences. ESG is about mitigating risk without measuring specific outcomes. Impact investing, on the other hands, directly quantifies societal impact and is value driven in its deployment of capital.
Big data can lead to big impact
Prior to this new fintech venture, Wilcox helped measure community impact while working for non-profits. He also served as a consultant using big data to help corporations solve ambiguous problems.
Wilcox said he began to question the impact of his own investments. Large institutional investors have access to research tools provided by MSCI or SustianAlytics, yet Wilcox failed to find any readily available tools for people like himself - ordinary investors. He wanted to combine the power of structured data with impact measurement to bring a new type of analysis to the average investor. He continues to build his platform, Ethos, with the vision of helping ordinary people make extraordinary investment decisions.
A world where impact investing works
If Wilcox were to construct a perfect world, where opportunities to invest with purpose were widely available, he would prioritize data transparency. Data is the key to accurately analyzing the impact your investment will have on local communities and the world at large. In today’s age, much of this data is available – for publicly traded companies with fat wallets. However, even this data is cluttered and hard to find.
Editor's note: Be sure to subscribe to our Brands Taking Stands newsletter, which comes out every Wednesday.
Wilcox envisions a world where impact data is easily accessible to all people and extends to organizations outside of the S&P 500. Imagine an integrated fund that blends affordable housing projects with a mix of corporate stocks. And he reiterated during his talk with 3p that he believes this world is possible and that culture will play a vital role in the process of change.
However, Wilcox cautions, “We need significant changes in the mindset of the entire investment community… to treat impact as an equal to risk and return.” Wilcox adds that he has an ambitious outlook on the future of investing and hopes to accelerate this movement with Ethos.
Ethos as a tool for effective impact investing
Ethos helps investors align investments with causes they care about – such as mental health, climate change, social justice, gender equality and healthcare. According to Wilcox, Ethos does the hard work of aggregating large amounts of data into a digestible manner. With easy to use software and a transparent methodology, Ethos is designed so investors can position their money with their values. While tools like Ethos are helpful, they are only one piece of the impact investing pie. What steps should you take, along the way, to put your money to good use?
A bit of advice for the impact investor
If you are searching for a more meaningful approach, Wilcox offers some advice. First, define what sort of impact you are trying to have: Do you want to make a difference on climate change, gender equality, racial justice or another cause or causes? Then, determine the risk you are willing to take with your money. If you seek low-risk strategies, focus on large publicly traded companies that behave ethically. If, on the other hand, you are willing to tolerate more risk, check for opportunities in your local community.
You may be wondering: how do I invest in my local community? Explore Impact Finance Center, a nonprofit academic center working to move money into social ventures at the community level. Alternatively, check in with your local bank to see if they offer any community-oriented investment funds. Lastly, reflect on your current positions. Can your money improve the world around you? Is your money improving the world around you? If you are ready… Ethos may be the tool to get started.
Image credit: Nattanan Kanchanaprat/Pixabay
ChargerHelp! Is on The Way – Providing Jobs and Improving Infrastructure for EVs


Fair or not, electric vehicles (EVs) still often come across as the preferred cars for rich white bros. Sure, federal and state tax incentives help lower the price tag, but affording that downpayment for most EVs requires plenty of coin, not to mention the monthly payments and insurance. Years after EVs supposedly entered the mainstream, the argument that they require little maintenance and no gas does not always help to move the needle for those in the middle- and lower-income groups.
But it is not just the drivers who make the world of EVs appear so white that if it were any whiter it would be see-through. The promise of a charging infrastructure may be enticing, but most EV charging stations are in office parks or in the parking lots of pricier retail stores like Whole Foods — again, overlooking many neighborhoods across the U.S. and large subsets of the population.
There's also a stubborn problem with the country's charging infrastructure: Estimates suggest that up to 25 percent of public EV charging stations are out of commission at any time — and repairing them is often an expensive prospect. But what if charging stations for EVs could be troubleshooted and repaired far more cost-effectively, while providing good-paying jobs in vulnerable communities? One startup believes it has the answer.
Editor's note: Be sure to subscribe to our Brands Taking Stands newsletter, which comes out every Wednesday.
ChargerHelp! says its on-demand charging station repair service is primed to tackle this ongoing challenge with EVs and can do so by meeting the demands of workforce development, adult learning and clean technology. Based in south Los Angeles, the company says it is working with residents in LA’s marginalized neighborhoods to equip them with the technology training and certification they need to repair charging stations.
“Our solution serves African American and LatinX communities specifically by increasing opportunities for those traditionally left behind and most marginalized to access digital and 21st-century skills, meet employer demands, and access the jobs of today and tomorrow,” the company recently said during a pitch at a recent MIT Solve competition.
ChargerHelp! is one of the social enterprises to be named this week as a top 15 solution in the Future of Work Grand Challenge, a $6 million prize competition led by the venture philanthropy organization New Profit, MIT Solve and JFF.
There will certainly be plenty of jobs that need to be filled in the coming decade if automakers’ plans to shift largely toward all-electric vehicles come to fruition. Currently there are 200,000 or so charging stations for EVs in the U.S. That number could surge to as many as 13 million by 2030, McKinsey predicts. That means more maintenance professionals will be needed coast to coast. And judging by the going rate of $175 for a three-hour site visit to troubleshoot and repair a charging station — even as the problem is frequently not an electrical one — the market will be ready for professionals who can repair these stations at a more economical rate, while at the same time these workers can make more than a living wage.
For now, ChargerHelp! and its app-based platform are operating as a pilot program in Los Angeles, but the startup’s co-founders say it has bold plans to expand to more states including Colorado, New York, Oregon and Washington.
“We just need to bridge the gap to the technology industry because it is fast growing, it is going to be robust, and we need to make sure that other communities are part of this growth spurt and this economic upturn that will happen to this industry,” said Evette Ellis, the chief workforce office and co-founder of ChargerHelp! in a recent pitch for funding, while also noting that her company has the potential to improve the overall experience of EVs for drivers.
Image credit: Ernest Ojeh/Unsplash
GM Dives Into Lithium-Metal Battery Technology
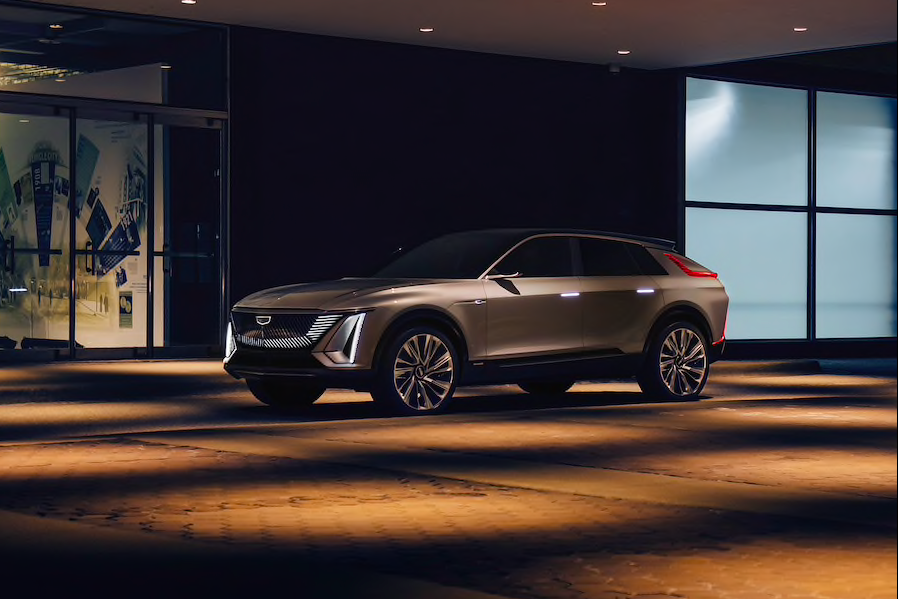
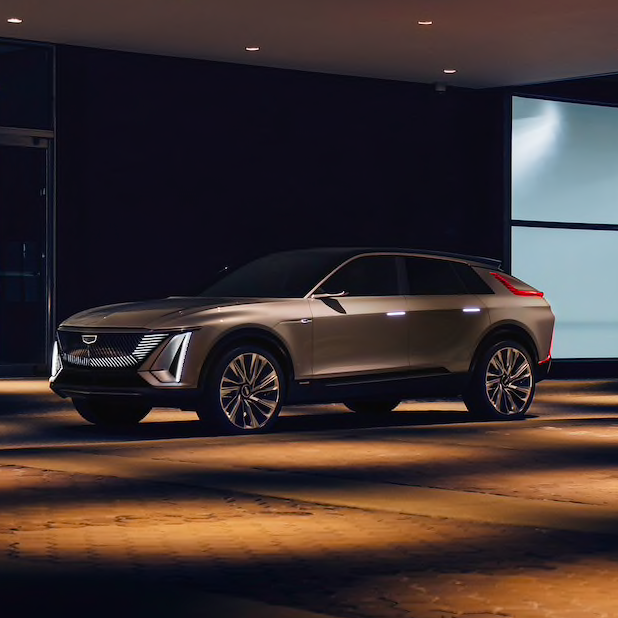


Photo: The all-electric Cadillac Lyriq, which GM says will have a range up to 300 miles per charge; this model is expected to roll out in the first half of 2022.
Later this year, General Motors will launch its first electric vehicles to use the company’s next generation Ultium EV platform. The first two GM releases using the automaker’s battery technology will be its flagship offerings, the GMC Hummer and the Cadillac Lyriq.
Following on from these two models, and because the Ultium platform is modular, GM says it will be able to rapidly build out an extensive range of 30 EVs by 2025, featuring vehicles across all of its brands and vehicle categories.
As these Ultium vehicles roll out, the platform will use familiar lithium-ion battery cells, but GM is already looking ahead to what comes next in battery technology. Last week, during a Washington Post live interview with GM’s president, Mark Reuss, GM announced that it has inked a joint agreement to develop lithium-metal batteries with Singapore-based SES (formerly known as SolidEnergy Systems).
Lithium-metal cells promise to unlock greater potential for EVs, making battery-powered vehicles an increasingly compelling choice. Lithium-metal batteries are lighter than lithium-ion ones and are able to deliver more energy per unit weight and volume. They achieve this by replacing the carbon anode used in a lithium-ion cell, with a lithium-metal anode instead. The lithium-metal anode is able to store more energy, which combined with its lighter weight promises significantly improved vehicle range.
For comparison purposes, GM’s Reuss says while the upcoming Hummer EV will be able to travel 350-plus miles on a lithium-ion equipped Ultium battery; future lithium-metal batteries will allow GM EVs to travel 500 to 600 miles on a single charge.
Furthermore, not only will lithium-metal batteries have the potential to achieve up to double the energy density, Reuss says the new batteries come at 60 percent of the cost of lithium-ion cells, asserting, “it’s a breakthrough.”
The new partnership is moving fast with the two companies planning to build a factory in Massachusetts to build prototypes of the new battery by 2023. What’s more, assuming development is successful, moving to lithium-metal will mesh well with GM’s modular platform approach.
This shift is possible as the Ultium platform was designed from the outset to be “backwards compatible.” When GM unveiled it last year, the company anticipated battery technology would continue to evolve rapidly and that new chemistries would certainly come along. Planning for Ultium to evolve with new battery developments was consequently an imperative for which it was well designed.
As a chemistry, lithium-metal is not new and has been expected for some time to be a promising alternative for vehicle batteries because of its superior performance. So far though, the technology has not reached prime time as it has not proved to be stable enough for safety, nor could it withstand as many charging cycles as lithium-ion batteries.
Already, tweaks to lithium-metal technology appear to be addressing battery cell stability and durability, indicating it will be an increasingly viable and important candidate for next generation vehicle batteries. Successful debugging of lithium-metal technology will be especially welcome as lithium-ion chemistry is beginning to reach the limits of possible improvements to energy density.
The new partnership GM is launching with SES is further evidence of the automaker’s commitment to electric vehicles. Reuss says they are all in on all-electric vehicles and at this point, the company has eschewed plug-in hybrids as a more cautious steppingstone away from gasoline powered vehicles. But will the automaker find customers?
Thankfully, for the company, GM has found customers of the Chevrolet Bolt EV - which has just undergone an update - to be the most loyal to the brand. This bodes well for its stated goal of an all-electric future as Reuss asserts the company has data showing there are many more customers ready to go all-electric.
That being said, he’s aware the automobile remains an emotive purchase and that a culture shift is underway. Reuss says, “Freedom and passion remain important, so GM will need to develop beautiful vehicles and reduce friction points for a very diverse country.”
If, as is anticipated, the next generation of battery technology delivers up to 600-mile range per charge at 60 percent of the cost, that’s got to help with its mission.
Image credit: Cadillac
How Companies Can Tackle the U.S. Housing Crisis


As the U.S. housing crisis grows even more dire due to the ongoing COVID-19 pandemic, key stakeholders within the wider real estate sector can support housing strategies that help ensure everyone has access to an affordable place to live. Even as the country moves closer to herd immunity and the rate of virus transmission has slowed, here’s the reality: Millions of Americans will be behind in rent - more than 11 million households, in fact - or will have to start all over and need to find a place to live that is within their means.
With as many as 5 million households facing the risk of eviction this year, bold action, targeted investments and creative solutions are needed.
To that end, be sure to join Mary Mazzoni, Senior Editor of TriplePundit, on Thursday, March 25 at 2 p.m. ET/11 a.m. PT as she sits down with Desiree Francis, Head of Community Finance at Capital One. Together, they will explore the challenges, complexities, and opportunities in financing Low Income Housing Tax Credit (LIHTC) developments in the United States as one way to tackle the nationwide housing crisis.
According to the U.S. Department of Housing and Urban Development (HUD), the LIHTC program is a leading resource for creating affordable housing in the U.S. Launched with the Tax Reform Act of 1986, the LIHTC program offers state and local LIHTC-allocating agencies the equivalent of approximately $8 billion in annual budget authority to issue tax credits for the acquisition, rehabilitation or new construction of rental housing specifically targeted to lower-income households. HUD data suggests that an average of close to 1,400 projects and 106,000 housing units have been made available annually between 1995 and 2018.
Joining Mazzoni and Francis will be Carol Galante, I. Donald Terner Professor in Affordable Housing and Urban Planning at the University of California, Berkeley to discuss findings from forthcoming Capital One-sponsored research completed by the university’s Terner Center.
Register for this free event here.
Image credit: Jacob Culp/Unsplash
Three Elements of Self-Care During a Pandemic


Prioritizing our wellbeing, as the world reels from the effects of COVID-19, has become a vital tool to aid recovery from the fallout of 2020.
As we all learn to adapt to the ‘new normal’ way of life, we are more conscious of our health and wellbeing than ever before. After all, a global pandemic is all-consuming, to say the very least.
Lockdowns have forced us to batten down the hatches and ensconce ourselves in the safety of our homes for long stretches of time, thus self-care has never been a hotter topic.
According to the American Psychological Association (APA), Americans have been severely affected by the Covid-19 pandemic, from education and work to the economy and health care. as well as the hardest hitting factors - deaths and long recoveries.
Nearly 8 in 10 adults (78 percent) have admitted the pandemic is a significant source of stress in their life, with 67 percent saying they have experienced increased stress over the course of the pandemic.
I have noticed when talking to family and friends, that they have become very focussed on three main areas of self-care: vitamins and herbs to support health; home spa treatments; and home cleaners and room sprays for a fresh, calm ambience.
Vitamins and herbs
One of the first steps to boost wellbeing is to take a daily vitamin to combat nutrient deficiencies. With the strain of this year taking its toll, eating healthily and sleeping well can sometimes fall by the wayside.
Vitamins and herbs should be free from pesticides and created using organic farming methods to benefit from their full potential.
Pure Synergy is a firm thatmanufactures all of its products in an award-winning, wind-powered, certified organic facility in Utah. Vitamins are made with organic ingredients, while quality and testing are supported by a certificate of compliance.
Gaia Herbs, nestled in the Blue Ridge Mountains of Western North Carolina,is another organic product company, committed to:
- Practicing Regenerative Farming
- Supporting Employee Wellbeing
- Positively Impacting Communities
- Encouraging Biodiversity
- Fostering Ecological Conservation
- Encouraging Recycling & Waste Reduction
- Promoting Watershed Health
Home spa treatments
While the thought of sharing a hot tub or a sauna with a bunch of strangers is extremely off-putting after the year we’ve endured, we still crave a bit of pampering to get us through the tougher, darker days - to calm both the body and mind.
May I present a new spa of choice – your home. While you won’t indulge in a professional treatment, there are many organic wellbeing products designed to destress and relax you. Slather it on, close your eyes, focus on your breathing and you could almost be at The Pearl Laguna, Laguna Beach, California.
An interest in organic formulations began as early as 1948 with Dr. Bronner’s peppermint castile soap. These days the 100 percent biodegradable soap is made with certified fair trade ingredients and organic hemp oil for a soft, smooth lather.Other companies started to follow suit with organic offerings.
JAMU’s tropical body care products blend organic, exotic ingredients and celebrate traditions to create a cross-cultural experience through Asian-inspired spa products and treatment rituals.The company creates organic oils and scrubs which are animal and cruelty-free (green beauty) and biodegradable (blue beauty).
EO is another company that has a collection of organic shower gels, natural bath, body, skin and hair care products, made with active botanicals and scented with pure essential oil.
Home cleaners and home sprays
If the home is clean and tidy, it has a more positive effect on mental health, which is vital to wellbeing now that we are all spending optimum time in our humble abodes.
With the pandemic placing an emphasis on home-cleaning to enhance the working from home experience, there is a wide range of environmentally friendly products to use. These can range from natural, non-toxic and eco-friendly to the most highly regulated organic.
A spray and a spritz can lighten the mental load - working and relaxing at home isn’t the easiest combination as it can be difficult to switch off, but with the right ambience, anything is achievable. Neil’s Yard Remedies offers organic aromatherapy room sprays that will lighten even the worst mood, for example.
Mrs Meyer’s Clean Day products are cruelty-free, made with essential oils and packaging is mostly recyclable (unfortunately the pumps and caps are not, at present). Created by a mother-of-nine in Iowa, the products are designed to smell of the garden and still be as efficient as its less sweet-smelling counterparts.
The method is another range with scents to make cleaning more pleasant while lowering the environmental impact. The firm isone of the fastest-growing private companies in America and covers all cleaning products from spray cleaners to dish soap – all non-toxic and mindful of the planet.
Seventh Generation aims to clean up the planet as well as the home with its eco-friendly, renewable plant-based products.All packaging is made with post-consumer recycled materials and the entire lifecycle of every single product is considered.
With 2021 waiting in the wings, a little wellbeing could help prepare us, whatever the future brings.
Sarah Walde is a research consultant for the New York team at Acre. To speak further about professional opportunities that may be on the horizon, please contact Sarah at sarah.walde@acre.com | Tel:+1 917 546 7096
Previously published on 3BL Media news.
Image credit: Anshu A/Unsplash
‘Isn’t It Bad to Cut Down Trees?’ and Other Burning Questions About Sustainable Forestry


Sheltering 80 percent of the world’s land biodiversity and sequestering twice as much carbon dioxide as they emit, forests easily make their case for preservation — a case made urgent by increasing deforestation. Though forests still cover about a third of the earth’s land area, they were almost twice as prevalent before human civilization emerged. Clearly, those that remain are worth protecting.
The good news is that organizations, individuals and businesses around the world are taking heed of these factors and transforming the way forests are managed. The Forest Stewardship Council (FSC) is one organization that’s working with stakeholders to restore ecosystems and certify products as responsibly sourced. Shoppers can also contribute to ensuring the sustainable management of forests by choosing products that display an FSC logo.

What the little tree logo on product packaging really means
We’ve all seen the FSC’s tree logo on products ranging from shoes to toilet paper to furniture. But what does it really mean for a product to come from responsibly managed forests and to be certified by the FSC?
The resources used to make an FSC-certified product are sourced from forests managed using a set of universal responsibility principles. These guidelines are applied specifically, based on the industry, environment and community. To be certified, forests are checked by independent auditors for compliance. The FSC system also includes a chain of custody certification that tracks materials and products through each step of their supply chains.
FSC has become the global standard for sustainable forest management. The idea gained momentum after the 1992 Rio Earth Summit failed to produce any international, legally binding commitment to combat deforestation. Instead, businesses, environmental organizations and community leaders formed a voluntary and market-based approach to preservation. As FSC members envisioned, consumer demand for sustainable products has risen over the years — and the number of certified forests and products increased in kind.
Now, over 25 years later, FSC members from economic, social and environmental chambers regularly convene to decide on appropriate standards for forest management. Members include labor unions, Indigenous tribes and associations, businesses, and environmental groups such as the WWF, the Nature Conservancy and Sierra Club.
“These groups come together, and through a process of negotiation and consensus define what responsible management means,” said Brad Kahn, director of communications for FSC U.S.
The FSC’s guiding principles cover the gamut of forest needs and services — from workers’ rights to Indigenous peoples’ rights to conservation values. To date, almost 500 million acres of forest have been certified, and 37,000 chain-of-custody certificates have been granted. The U.S. alone is home to over 35 million certified acres, and nearly 4,000 U.S. companies have gained chain-of-custody certification for a material or product. Brands such as Allbirds, Burton, Charmin, Patagonia and many others source from FSC-certified forests.
The shopper’s role: Look out for the FSC tree
Shoppers have a significant role to play in the FSC’s vision of meeting the world’s need for forest products without compromising forest health.
“By looking for the FSC logo on the products they buy, consumers can really help protect forests as forests, even as they use products from those forests every day,” Kahn says. “There’s a lot of things in the world that are very difficult to make a difference on — buying FSC-certified products with the logo on it [is] a simple action with a profound impact for consumers to try to make the world a better place.”
Hands-off doesn’t necessarily mean healthier forests
Before we dive into what exactly goes into responsible forest management, it’s important to clarify a common misconception about forest well-being: the assumption that forests are best off without human intervention, in a bubble unspoiled by the outside world.
Kahn has a few words to offer in response. In an era defined by human activity, there’s no such thing as a forest untouched by human impact, Kahn tells TriplePundit: “We are managing forests,” he explained. “We just need to be explicit about it so that we achieve the kinds of outcomes that we're hoping to achieve — whether those are environmental protections, social protections, or economic outputs like timber and pulp.”
Even the concept of an untouched forest is flawed at the outset, Kahn notes: For example, Indigenous peoples have lived in North America for thousands of years, all while engaging deliberately in forest management.
Managing forests to prevent deforestation
It may seem counter-intuitive, but supporting economic activity in forests ensures they are more likely to remain forests. To understand why, it’s important to note ownership. “In a place like the United States, the vast majority of [forested] land is privately owned, and people need to earn a living,” Kahn explains. “If they can earn a living from managing their forests, then they have an incentive to keep those forests as forests.” Alternatively, landowners are more likely to sell their forested land to developers if they can't find a way to earn a living from it.
Approximately half of the hundreds of millions of acres of forested land in the U.S. is privately owned — and over half of those forests are owned by families and individuals. FSC’s 10 principles and 70 criteria for responsible forestry help landowners of all sizes make their forests economically viable and healthy — goals that go hand-in-hand.
Logging isn’t the only business option. Hunting, recreation, mushroom harvesting, fuel wood gathering, carbon storage and clean drinking water are some of the economic opportunities Kahn lists as examples.
Forests: Carbon problem or climate solution?
Of course, the ultimate goal of managing forests responsibly is to stave off global crises such as climate change. "Forests are right now both a cause and a solution to climate change,” Kahn says. “They're a cause because deforestation — and what's called conversion of forests to other things like agriculture, ranching or housing developments — is causing a lot of carbon emissions.”
On the other hand, “One of the most powerful things we can do to fight climate change is allow our forests to grow a little bit older … and then also look for reforestation and planting trees where there used to be forests,” he explains. “Growing trees offers a lot of potential to store carbon and fight climate change.”
Contrary to popular belief, forest restoration often requires very hands-on management to achieve the conditions that support wildlife, clean water and store carbon, he explains. Even within the few decades of the FSC’s existence — a trivial amount of time to most trees — businesses have already begun to invest in reforestation, but there is still more work to do and benefits to realize. Recent research indicates that global reforestation programs could remove two-thirds of all the manmade emissions in the atmosphere today, a figure scientists described as “mind-blowing.”
“The potential is literally everywhere — the entire globe,” said Tom Crowther, a professor at the Swiss university ETH Zürich, who led the research. “Every one of us can get involved.”
This article series is sponsored by Procter & Gamble and produced by the TriplePundit editorial team.
Image credit: Liam Pozz/Unsplash and Procter & Gamble
The SDGs: What Does It Look Like to Make Progress on Climate Action?
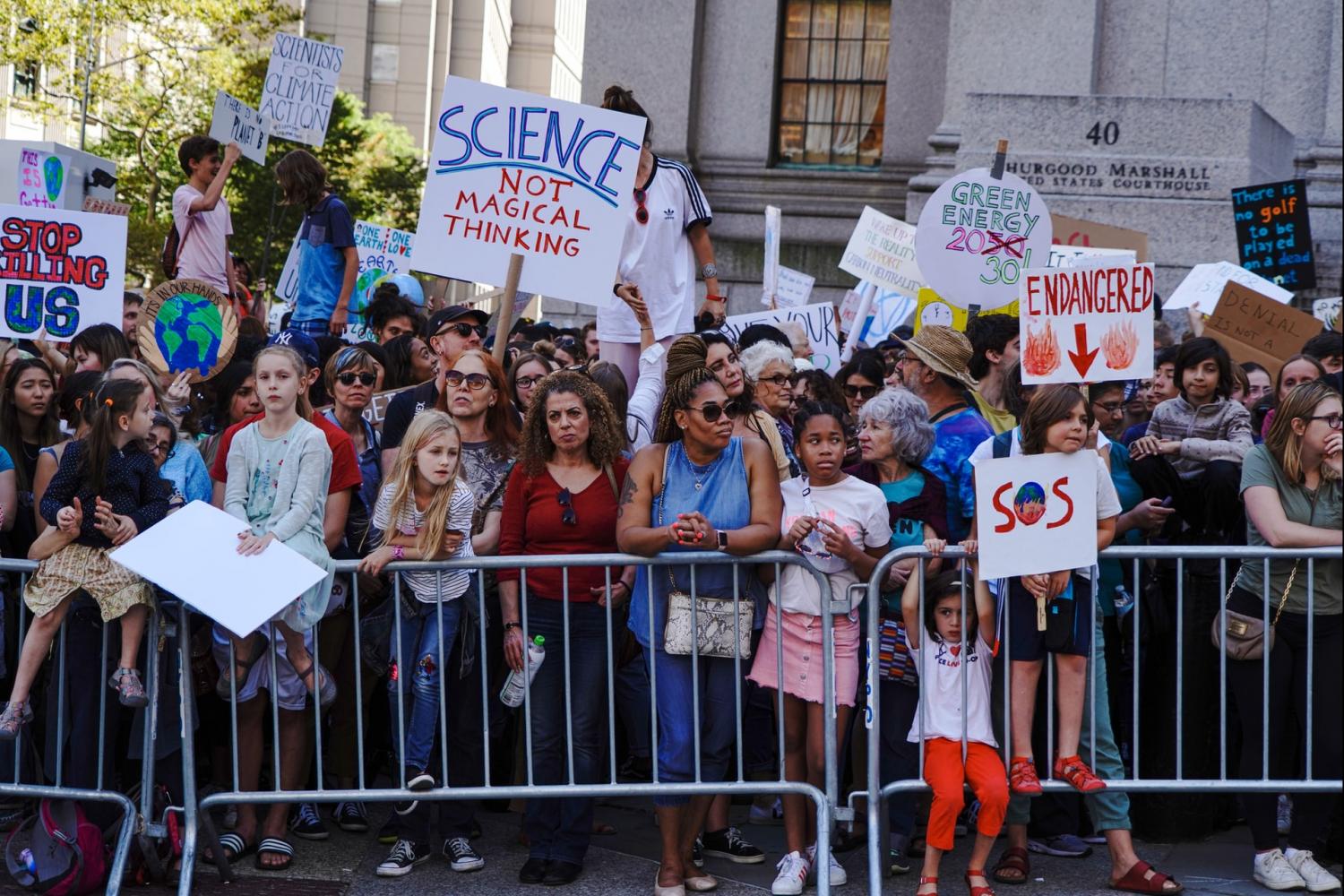
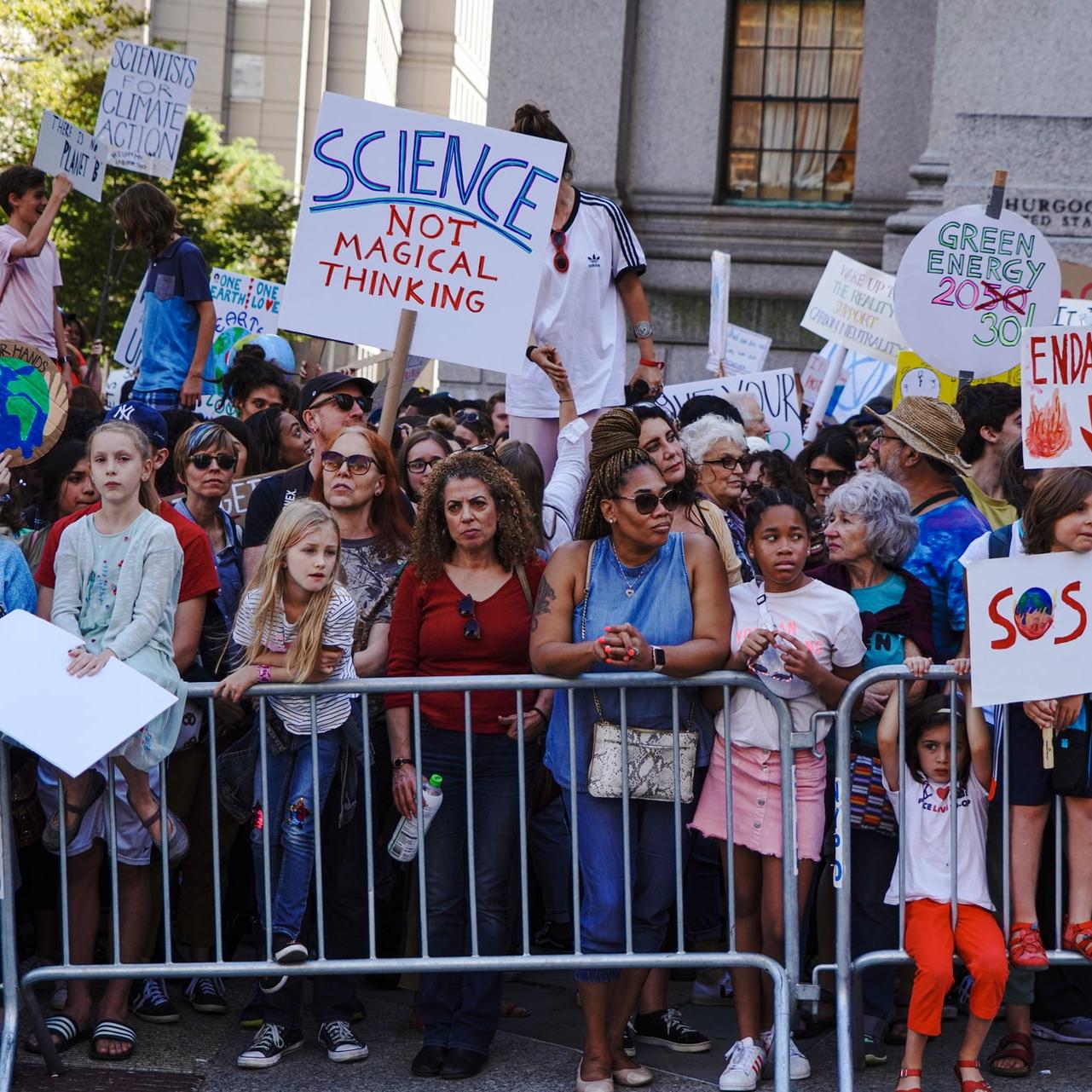
Photo: Protesters urging bolder climate action during Climate Week in New York City in September 2019. One of the UN’s SDGs in particular focuses on climate action and resilience planning.
The Biden administration has been vocal about prioritizing climate action throughout the executive branch, including appointing the first ever Special Presidential Envoy for Climate, John Kerry, who has mostly recently been in talks with European leaders about climate action. The timing couldn’t be more urgent.
Recent analysis shows that the U.S. will need to cut carbon emissions by at least 57 percent of 2005 levels by 2030 to meet the Biden administration’s goal of net-zero emissions by 2050. In 2016, when the U.S. signed the Paris Climate Agreement, the target was 26 to 28 percent reductions by 2025, but those efforts were reversed under the Trump administration. In April 2021, nations will announce new 2030 goals for the Paris Agreement, which the U.S. rejoined in January.
Further setbacks have been noted in the Sustainable Development Goals, or SDGs, a series of 17 goals set by the United National General Assembly in 2015 for the world to achieve by 2030. From eradicating poverty and hunger to tackling the climate crisis, the SDGs attempt to address the most fundamental challenges faced by society. In a recent GlobeScan/SustainAbility survey of 700 experts from business, government, NGOs and academics from 71 countries, 94 percent of respondents listed climate change as the most urgent societal challenge. Unfortunately, in a follow up survey, 61 percent of respondents felt like progress on the climate action (SDG 13) has been poor.
All of these targets are goals that feel lofty and overwhelming. What does it actually mean to make progress on SDGs and climate action?
Climate action as part of the SDGs
The 13th SDG, focused on climate action, sounds straightforward enough: Take urgent action to combat climate change and its impacts. But to be measurable - and therefore successful - there must be smaller steps leading up to that. Within each SDG are targets. For climate action, they include: strengthening resilience and adaptive capacity to climate-related disasters; the integration of climate change measures into policy and planning; building knowledge and capacity to meet climate change; implement the UN Framework Convention on Climate Change, and work on promoting mechanisms to raise capacity for such planning and management.
These are all still high-level, and they are meant to be. Every country will need to figure out its pathway to meeting the goal in the way that makes the most sense to its government and economy. Judging by the amount of work that still needs to be done in the U.S. to meet climate targets (which can feed into the SDGs), it will be a heavy lift. Unfortunately, earlier climate action could have mitigated some of that, but we are now at the point where deep dives are necessary. Luckily, during the past four years, while the U.S. federal government bowed out of and discussion of climate action, the private sector kept pushing ahead, and will continue to be instrumental in getting the U.S. to the finish line.
A look at climate resilience
Take, for example, the resilience and adaptive capacity target within the climate action SDG. Reaching that target will require national disaster risk management plans and local disaster risk management. A national disaster risk management plan will ideally be a policy that addresses all stages of disaster risk management using a multi-sectoral approach that should include the public and private sector stakeholders engaged in policies and practices related to education, health, law enforcement, finance, trade, tourism, agriculture, transportation, energy and water.
Some industries have already been proactive about including plans to address climate risk into their portfolios. The reinsurance industry, for example, which insures the insurers, has for years pushed for better accounting for climate risk. With a high degree of risk, especially in areas such as coastal and riparian communities across the U.S., reinsurers have been vocal about the fact that not considering climate change will lead to an untenable situation with mortgages, home insurance, and pensions, and could spell disaster for the insurance industry as a whole. With $15 trillion of assets at risk from coastal flooding alone, the industry cannot afford to underestimate the risk.
With a reenergized federal government keeping its eye on the ball, aiming to engage every executive agency in the climate battle, it is clear that regulations, expectations, and targets must be set so that the private sector can be a successful and powerful team player. The only way to meet the Paris Agreement goals and the SDGs is by making it a national commitment. No one gets to sit this game out.
Image credit: Katie Rodriguez/Unsplash